Antihuman factor VIII C2 domain antibodies in hemophilia A mice recognize a functionally complex continuous spectrum of epitopes dominated by inhibitors of factor VIII activation
- PMID: 17848617
- PMCID: PMC2234776
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-096842
Antihuman factor VIII C2 domain antibodies in hemophilia A mice recognize a functionally complex continuous spectrum of epitopes dominated by inhibitors of factor VIII activation
Abstract
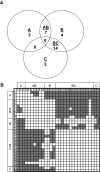
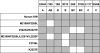
The diversity of factor VIII (fVIII) C2 domain antibody epitopes was investigated by competition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a panel of 56 antibodies. The overlap patterns produced 5 groups of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), designated A, AB, B, BC, and C, and yielded a set of 18 distinct epitopes. Group-specific loss of antigenicity was associated with mutations at the Met2199/Phe2200 phospholipid binding beta-hairpin (group AB MAbs) and at Lys2227 (group BC MAbs), which allowed orientation of the epitope structure as a continuum that covers one face of the C2 beta-sandwich. MAbs from groups A, AB, and B inhibit the binding of fVIIIa to phospholipid membranes. Group BC was the most common group and displayed the highest specific fVIII inhibitor activities. MAbs in this group are type II inhibitors that inhibit the activation of fVIII by either thrombin or factor Xa and poorly inhibit the binding of fVIII to phospholipid membranes or von Willebrand factor (VWF). Group BC MAbs are epitopically and mechanistically distinct from the extensively studied group C MAb, ESH8. These results reveal the structural and functional complexity of the anti-C2 domain antibody response and indicate that interference with fVIII activation is a major attribute of the inhibitor landscape.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High-affinity, noninhibitory pathogenic C1 domain antibodies are present in patients with hemophilia A and inhibitors.Blood. 2016 Oct 20;128(16):2055-2067. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-701805. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27381905 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-C1 domain antibodies that accelerate factor VIII clearance contribute to antibody pathogenicity in a murine hemophilia A model.J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1779-1788. doi: 10.1111/jth.14233. Epub 2018 Aug 13. J Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29981270 Free PMC article.
-
Nonclassical anti-C2 domain antibodies are present in patients with factor VIII inhibitors.Blood. 2008 Aug 15;112(4):1151-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-132639. Epub 2008 May 21. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18495957 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope specificity and inactivation mechanisms of factor VIII inhibitor antibodies.Vox Sang. 1999;77 Suppl 1:17-20. doi: 10.1159/000056708. Vox Sang. 1999. PMID: 10529680 Review.
-
Properties of anti-factor VIII inhibitor antibodies in hemophilia A patients.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26(2):137-42. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-9815. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000. PMID: 10919405 Review.
Cited by
-
Removal of single-site N-linked glycans on factor VIII alters binding of domain-specific monoclonal antibodies.J Thromb Haemost. 2022 Mar;20(3):574-588. doi: 10.1111/jth.15616. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 34863021 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-binding properties of the Factor VIII C2 domain.Biochem J. 2011 Apr 1;435(1):187-96. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101797. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21210768 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid binding lowers immunogenicity of human recombinant factor VIII in von Willebrand factor knockout mice.Thromb Haemost. 2011 Jun;105(6):1115-8. doi: 10.1160/TH10-09-0628. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Thromb Haemost. 2011. PMID: 21475771 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intravenous administration of Factor VIII-O-Phospho-L-Serine (OPLS) complex reduces immunogenicity and preserves pharmacokinetics of the therapeutic protein.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan 23;66:157-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.10.010. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25459532 Free PMC article.
-
The 1.7 Å X-ray crystal structure of the porcine factor VIII C2 domain and binding analysis to anti-human C2 domain antibodies and phospholipid surfaces.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0122447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122447. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lusher JM, Arkin S, Abildgaard CF, Schwartz RS the Kogenate Previously Untreated Patient Study Group. Recombinant factor VIII for the treatment of previously untreated patients with hemophilia A: safety, efficacy, and the development of inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:453–459. - PubMed
-
- Bray GL, Gomperts ED, Courtier S, et al. A multicenter study of recombinant factor VIII (Recombinate): safety, efficacy, and inhibitor risk in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A. Blood. 1994;83:2428–2435. - PubMed
-
- Lusher JM, Lee CA, Kessler CM, Bedrosian CL the Refacto Phase 3 Study Group. The safety and efficacy of B-domain deleted recombinant factor VIII concentrate in patients with severe haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2003;9:38–49. - PubMed
-
- Kreuz W, Ettingshausen CE, Zyschka A, et al. Inhibitor development in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A: a prospective long-term follow-up comparing plasma-derived and recombinant products. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2002;28:285–290. - PubMed
-
- Lollar P, Parker CG. Subunit structure of thrombin-activated porcine factor VIII. Biochemistry. 1989;28:666–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

