Salmonella induces prominent gene expression in the rat colon
- PMID: 17850650
- PMCID: PMC2048963
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-84
Salmonella induces prominent gene expression in the rat colon
Abstract
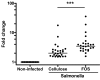
Background: Salmonella enteritidis is suggested to translocate in the small intestine. In vivo it induces gene expression changes in the ileal mucosa and Peyer's patches. Stimulation of Salmonella translocation by dietary prebiotics fermented in colon suggests involvement of the colon as well. However, effects of Salmonella on colonic gene expression in vivo are largely unknown. We aimed to characterize time dependent Salmonella-induced changes of colonic mucosal gene expression in rats using whole genome microarrays. For this, rats were orally infected with Salmonella enteritidis to mimic a foodborne infection and colonic gene expression was determined at days 1, 3 and 6 post-infection (n = 8 rats per time-point). As fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) affect colonic physiology, we analyzed colonic mucosal gene expression of FOS-fed versus cellulose-fed rats infected with Salmonella in a separate experiment. Colonic mucosal samples were isolated at day 2 post-infection.
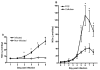
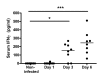
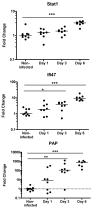
Results: Salmonella affected transport (e.g. Chloride channel calcium activated 6, H+/K+ transporting Atp-ase), antimicrobial defense (e.g. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein, Defensin 5 and phospholipase A2), inflammation (e.g. calprotectin), oxidative stress related genes (e.g. Dual oxidase 2 and Glutathione peroxidase 2) and Proteolysis (e.g. Ubiquitin D and Proteosome subunit beta type 9). Furthermore, Salmonella translocation increased serum IFN gamma and many interferon-related genes in colonic mucosa. The gene most strongly induced by Salmonella infection was Pancreatitis Associated Protein (Pap), showing >100-fold induction at day 6 after oral infection. Results were confirmed by Q-PCR in individual rats. Stimulation of Salmonella translocation by dietary FOS was accompanied by enhancement of the Salmonella-induced mucosal processes, not by induction of other processes.
Conclusion: We conclude that the colon is a target tissue for Salmonella, considering the abundant changes in mucosal gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Naughton PJ, Grant G, Spencer RJ, Bardocz S, Pusztai A. A rat model of infection by Salmonella typhimurium or Salm. enteritidis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1996;81:651–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

