Optimising the use of computed radiography in pediatric chest imaging
- PMID: 17851716
- PMCID: PMC3043687
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-007-9071-2
Optimising the use of computed radiography in pediatric chest imaging
Abstract
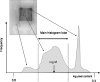
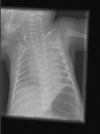
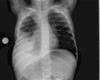
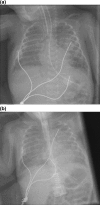
The objective of this study was to analyze image quality of chest examinations in pediatric patients using computed radiography (CR) obtained with a wide range of doses to suggest the appropriate parameters for optimal image quality. A sample of 240 chest images in four age ranges was randomly selected from the examinations performed during 2004. Images were obtained using a CR system and were evaluated independently by three radiologists. Each image was scored using criteria proposed by the European Guidelines on Quality Criteria in Pediatrics. Mean global scoring and scoring of individual criteria more sensitive to noise were used to evaluate image quality. Agfa dose level (DL) was in the range 1.20 to 2.85. It was found that there was not significant correlation (R < 0.5) between image quality and DL for any of the age ranges for either global score or for individual criteria more related to noise. The mean value of DL was in the ranges 1.9-2.1 for the four age bands. From this study, a DL value of 1.6 is proposed for pediatric CR chest imaging. This could yield a reduction of approximately a factor of 2.5 in mean patient entrance surface doses.
Figures




Comment in
-
Letter to the editor re: "Optimizing the use of computer radiography in pediatric chest imaging".J Digit Imaging. 2009 Apr;22(2):99-100; author reply 101-2. doi: 10.1007/s10278-008-9137-9. Epub 2008 Jul 12. J Digit Imaging. 2009. PMID: 18622641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Low-dose digital computed radiography in pediatric chest imaging.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Oct;151(4):775-9. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.4.775. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988. PMID: 3262278
-
Radiation dose reduction with hybrid iterative reconstruction for pediatric CT.Radiology. 2012 May;263(2):537-46. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110268. Radiology. 2012. PMID: 22517962
-
Comparative study between mobile computed radiography and mobile flat-panel radiography for bedside chest radiography: impact of an antiscatter grid on the visibility of selected diagnostically relevant structures.Invest Radiol. 2014 Jan;49(1):1-6. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182a56654. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24019019
-
Pediatric computed tomographic angiography: imaging the cardiovascular system gently.Radiol Clin North Am. 2010 Mar;48(2):439-67, x. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.03.005. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20609882 Review.
-
[CR image-processing technology in a chest domain].Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2006 Jul 20;62(7):895-900. doi: 10.6009/jjrt.62.895. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 16906676 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
BO-CLAHE enhancing neonatal chest X-ray image quality for improved lesion classification.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 10;15(1):4931. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88451-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39929905 Free PMC article.
-
Digital radiography exposure indices: A review.J Med Radiat Sci. 2014 Jun;61(2):112-8. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.49. Epub 2014 May 11. J Med Radiat Sci. 2014. PMID: 26229645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normalizing Heterogeneous Medical Imaging Data to Measure the Impact of Radiation Dose.J Digit Imaging. 2015 Dec;28(6):671-83. doi: 10.1007/s10278-015-9805-5. J Digit Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26013637 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose optimisation for conventional imaging in infants and newborns using automatic dose management software: an application of the new 2013/59 EURATOM directive.Br J Radiol. 2018 Jun;91(1086):20180022. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180022. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29537302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Commission Council directive 97/43/Euratom health protection of individuals against the dangers of ionizing radiation in relation to medical exposure. Off J Eur Communities. 1997;L180:22–27.
-
- Peters SE, Brennan PC. Digital radiography: are the manufacturers’ settings too high? Optimisation of the Kodak digital radiography system with aid of the computed radiography dose index. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(9):2381–2387. - PubMed
-
- Commission of the European Communities: European guidelines on quality criteria for diagnostic radiographic images in pediatrics. (Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg), Report EUR 16261. CEC 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

