MK-801 upregulates NR2A protein levels and induces functional recovery of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm following acute C2 hemisection in adult rats
- PMID: 17853656
- PMCID: PMC2031932
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2007.11753950
MK-801 upregulates NR2A protein levels and induces functional recovery of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm following acute C2 hemisection in adult rats
Abstract
Background: C2 hemisection results in paralysis of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm. Recent data indicate that an upregulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor 2A subunit following chronic C2 hemisection is associated with spontaneous hemidiaphragmatic recovery following injury. MK-801, an antagonist of the NMDA receptor, upregulates the NR2A subunit in neonatal rats.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that administration of MK-801 to adult, acute C2-hemisected rats would result in an increase of NR2A in the spinal cord. Furthermore, we hypothesized that upregulation of NR2A would be associated with recovery of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm as in the chronic studies.
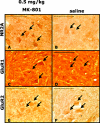
Design: To develop a dose-response curve, adult rats were treated with varying doses of MK-801 and their spinal cords harvested and assessed for NR2A as well as AMPA GluR1 and GluR2 subunit protein levels. In the second part of this study, C2-hemisected animals received MK-801. Following treatment, the animals were assessed for recovery of the hemidiaphragm through electromyographic recordings and their spinal cords assessed for NR2A, GluR1, and GluR2.
Results: Treatment with MK-801 leads to an increase of the NR2A subunit in the spinal cords of adult noninjured rats. There were no changes in the expression of GluR1 and GluR2 in these animals. Administration of MK-801 to C2-hemisected rats resulted in recovery of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm, an increase of NR2A, and a decrease of GluR2.
Conclusion: Our findings strengthen the evidence that the NR2A subunit plays a substantial role in mediating recovery of the paralyzed hemidiaphragm following C2 spinal cord hemisection.
Figures
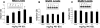


References
-
- Dobbins EG, Feldman JL. Brainstem network controlling descending drive to phrenic motoneurons in rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994;347:64–86. - PubMed
-
- Goshgarian HG, Guth L. Demonstration of functionally ineffective synapses in the guinea pig spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 1977;57:613–621. - PubMed
-
- Nantwi KD, El Bohy A, Goshgarian HG. Actions of systemic theophylline on hemidiaphragmatic recovery in rats following cervical spinal cord hemisection. Exp Neurol. 1996;140:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Zhou SY, Goshgarian HG. Effects of serotonin on crossed phrenic nerve activity in cervical spinal cord hemisection in cervical spinal cord hemisected rats. Exp Neurol. 1999;160:446–453. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
