Rumble in the nuclear jungle: compartmentalization, trafficking, and nuclear action of plant immune receptors
- PMID: 17853890
- PMCID: PMC2034664
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601854
Rumble in the nuclear jungle: compartmentalization, trafficking, and nuclear action of plant immune receptors
Abstract
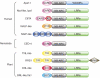
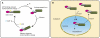
Plants and animals have evolved structurally related innate immune sensors inside cells to detect the presence of microbial molecules. An evolutionary ancient folding machinery becomes engaged for the synthesis of autorepressed receptor forms in both kingdoms. The receptors act as regulatory signal transduction switches and are activated upon direct or indirect perception of non-self structures. Recent findings indicate that nucleo-cytoplasmic partitioning and nuclear activity is critical for the function of several plant immune sensors, thereby linking receptor function to transcriptional reprogramming of host cells for pathogen defense. This implies short signalling pathways and reveals parallels with regulatory control mechanisms of animal steroid receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Aravind L (2000) The BED finger, a novel DNA-binding domain in chromatin-boundary-element-binding proteins and transposases. Trends Biochem Sci 25: 421–423 - PubMed
-
- Azevedo C, Sadanandom A, Kitagawa K, Freialdenhoven A, Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P (2002) The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R Gene-triggered disease resistance. Science 295: 2073–2076 - PubMed
-
- Bartsch M, Gobbato E, Bednarek P, Debey S, Schultze JL, Bautor J, Parker JE (2006) Salicylic acid-independent ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 signaling in Arabidopsis immunity and cell death is regulated by the monooxygenase FMO1 and the nudix hydrolase NUDT7. Plant Cell 18: 1038–1051 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bateman A, Bycroft M (2000) The structure of a LysM domain from E coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J Mol Biol 299: 1113–1119 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

