Direct stimulation of receptor-controlled phospholipase D1 by phospho-cofilin
- PMID: 17853892
- PMCID: PMC2230846
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601852
Direct stimulation of receptor-controlled phospholipase D1 by phospho-cofilin
Abstract
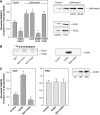
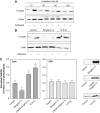
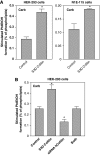
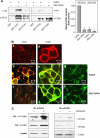
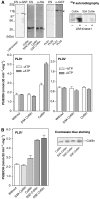
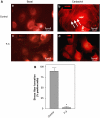
The activity state of cofilin, which controls actin dynamics, is driven by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle. Phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinases results in its inactivation, a process supported by 14-3-3zeta and reversed by dephosphorylation by slingshot phosphatases. Here we report on a novel cellular function for the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle of cofilin. We demonstrate that muscarinic receptor-mediated stimulation of phospholipase D1 (PLD1) is controlled by LIM-kinase, slingshot phosphatase as well as 14-3-3zeta, and requires phosphorylatable cofilin. Cofilin directly and specifically interacts with PLD1 and upon phosphorylation by LIM-kinase1, stimulates PLD1 activity, an effect mimicked by phosphorylation-mimic cofilin mutants. The interaction of cofilin with PLD1 is under receptor control and encompasses a PLD1-specific fragment (aa 585-712). Expression of this fragment suppresses receptor-induced cofilin-PLD1 interaction as well as PLD stimulation and actin stress fiber formation. These data indicate that till now designated inactive phospho-cofilin exhibits an active cellular function, and suggest that phospho-cofilin by its stimulatory effect on PLD1 may control a large variety of cellular functions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interplay between components of a novel LIM kinase-slingshot phosphatase complex regulates cofilin.EMBO J. 2005 Feb 9;24(3):473-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600543. Epub 2005 Jan 20. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15660133 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Salmonella entry requires activity cycles of host ADF and cofilin.Cell Microbiol. 2004 May;6(5):459-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00375.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15056216
-
InlB-mediated Listeria monocytogenes internalization requires a balanced phospholipase D activity maintained through phospho-cofilin.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Aug;81(4):860-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07726.x. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21722201
-
Signaling mechanisms and functional roles of cofilin phosphorylation and dephosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Feb;25(2):457-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23153585 Review.
-
Ultrasensitivity in the Cofilin Signaling Module: A Mechanism for Tuning T Cell Responses.Front Immunol. 2016 Feb 19;7:59. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00059. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26925064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple facets of cAMP signalling and physiological impact: cAMP compartmentalization in the lung.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2012 Nov 30;5(12):1291-331. doi: 10.3390/ph5121291. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24281338 Free PMC article.
-
Increased actin polymerization and stabilization interferes with neuronal function and survival in the AMPKγ mutant Loechrig.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 25;9(2):e89847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089847. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587072 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrus orbiculatus extract suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by mediating cytoskeleton rearrangement via inhibition of the Cofilin 1 signaling pathway in human gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):2926-2932. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6470. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28927046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phospholipase D in parathyroid hormone type 1 receptor signaling and trafficking.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Dec;23(12):2048-59. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0436. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19837945 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-canonical Pathway with Potential for Safer Modulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Steroid-Resistant Airway Diseases.iScience. 2019 Feb 22;12:232-246. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.01.023. Epub 2019 Jan 21. iScience. 2019. PMID: 30711747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acevedo K, Moussi N, Li R, Soo P, Bernard O (2006) LIM kinase 2 is widely expressed in all tissues. J Histochem 54: 487–501 - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR (1999) Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15: 185–230 - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR, Wiggan OP (2002) ADF/cofilin and actin dynamics in disease. Trends Cell Biol 12: 598–605 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalina cells. Science 296: 550–553 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

