Calcium signalling and cell-fate choice in B cells
- PMID: 17853903
- PMCID: PMC2743935
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2172
Calcium signalling and cell-fate choice in B cells
Abstract
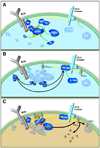
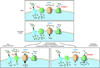
Alterations in the cytosolic concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) transmit information that is crucial for the development and function of B cells. Cytosolic Ca2+ concentration is determined by a balance of active transport and gradient-driven Ca2+ fluxes, both of which are subject to the influence of multiple receptors and environmental sensing pathways. Recent advances in genomics have allowed for the compilation of an increasingly comprehensive list of Ca2+ transporters and channels expressed by B cells. The increasing understanding of the function and regulation of these proteins has begun to shift the frontier of Ca2+ physiology in B cells from molecular analysis to determining how diverse inputs to cytosolic Ca2+ concentration are integrated in specific immunological contexts.
Figures




References
-
- Quintana A, Griesemer D, Schwarz EC, Hoth M. Calcium-dependent activation of T-lymphocytes. Pflugers Arch. 2005;450:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Lewis RS. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:497–521. - PubMed
-
- Cahalan MD, Wulff H, Chandy KG. Molecular properties and physiological roles of ion channels in the immune system. J Clin Immunol. 2001;21:235–252. - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Betz A, Wegmeyer H. Divergent and convergent signaling by the diacylglycerol second messenger pathway in mammals. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14:328–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI45901/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM078195/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064316/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI044259/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD037091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD37091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045901/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA81140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM64316/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL07543/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044259/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM64091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

