PathFinder: mining signal transduction pathway segments from protein-protein interaction networks
- PMID: 17854489
- PMCID: PMC2100073
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-335
PathFinder: mining signal transduction pathway segments from protein-protein interaction networks
Abstract
Background: A Signal transduction pathway is the chain of processes by which a cell converts an extracellular signal into a response. In most unicellular organisms, the number of signal transduction pathways influences the number of ways the cell can react and respond to the environment. Discovering signal transduction pathways is an arduous problem, even with the use of systematic genomic, proteomic and metabolomic technologies. These techniques lead to an enormous amount of data and how to interpret and process this data becomes a challenging computational problem.
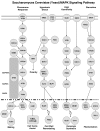
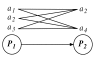
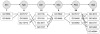
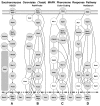
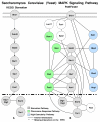
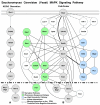
Results: In this study we present a new framework for identifying signaling pathways in protein-protein interaction networks. Our goal is to find biologically significant pathway segments in a given interaction network. Currently, protein-protein interaction data has excessive amount of noise, e.g., false positive and false negative interactions. First, we eliminate false positives in the protein-protein interaction network by integrating the network with microarray expression profiles, protein subcellular localization and sequence information. In addition, protein families are used to repair false negative interactions. Then the characteristics of known signal transduction pathways and their functional annotations are extracted in the form of association rules.
Conclusion: Given a pair of starting and ending proteins, our methodology returns candidate pathway segments between these two proteins with possible missing links (recovered false negatives). In our study, S. cerevisiae (yeast) data is used to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Figures
References
-
- Fields S, Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989;340:245–246. - PubMed
-
- Uetz P, Giot L, Cagney G, Mansfield TA, Judson RS, Knight JR, Lockshon D, Narayan V, Srinivasan M, Pochart P, Qureshi-Emili A, Li Y, Godwin B, Conover D, Kalbfleisch T, Vijayadamodar G, Yang M, Johnston M, Fields S, Rothberg JM. A comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 2000;403:623–627. - PubMed
-
- Reboul J, Vaglio P, Rual JF, Lamesch P, Martinez M, Armstrong CM, Li S, Jacotot L, Bertin N, Janky R, Moore T, Hudson JR, Hartley JL, Brasch MA, Vandenhaute J, Boulton S, Endress GA, Jenna S, Chevet E, Papasotiropoulos V, Tolias PP, Ptacek J, Snyder M, Huang R, Chance MR, Lee H, Doucette-Stamm L, Hill DE, Vidal M. C. elegans ORFeome version 1.1: experimental verification of the genome annotation and resource for proteome-scale protein expression. Nat Genet. 2003;34:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Giot L, et al. A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2003;302:1727–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

