Structure-function analysis of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein - is the whole a sum of its parts?
- PMID: 17854503
- PMCID: PMC2082274
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-2-26
Structure-function analysis of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein - is the whole a sum of its parts?
Abstract
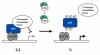
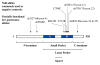
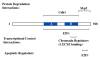
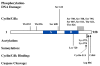
Biochemical analysis of the retinoblastoma protein's function has received considerable attention since it was cloned just over 20 years ago. During this time pRB has emerged as a key regulator of the cell division cycle and its ability to block proliferation is disrupted in the vast majority of human cancers. Much has been learned about the regulation of E2F transcription factors by pRB in the cell cycle. However, many questions remain unresolved and researchers continue to explore this multifunctional protein. In particular, understanding how its biochemical functions contribute to its role as a tumor suppressor remains to be determined. Since pRB has been shown to function as an adaptor molecule that links different proteins together, or to particular promoters, analyzing pRB by disrupting individual protein interactions holds tremendous promise in unraveling the intricacies of its function. Recently, crystal structures have reported how pRB interacts with some of its molecular partners. This information has created the possibility of rationally separating pRB functions by studying mutants that disrupt individual binding sites. This review will focus on literature that investigates pRB by isolating functions based on binding sites within the pocket domain. This article will also discuss the prospects for using this approach to further explore the unknown functions of pRB.
Figures

References
-
- Dyson N. The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 1998;12: 2245–2262. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

