Effect of chronic administration of ethanol on the regulation of the delta-subunit of GABA(A) receptors in the rat brain
- PMID: 17854781
- PMCID: PMC2278031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.07.077
Effect of chronic administration of ethanol on the regulation of the delta-subunit of GABA(A) receptors in the rat brain
Abstract
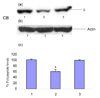
In the present study, we investigated the effect of chronic ethanol (CE) administration on the polypeptide levels of the delta-subunit of GABA(A) receptors and [(3)H]muscimol binding to the immunoprecipitated delta-subunit-containing GABA(A) receptor assemblies in the rat brain. CE administration resulted a down-regulation of polypeptide levels of the delta-subunit of GABA(A) receptors in the rat cerebellum and hippocampus, whereas there were no changes in the delta-subunit polypeptide levels in the rat cerebral cortex. Further, CE administration caused a down-regulation of native delta-subunit-containing GABA(A) receptor assemblies in the rat cerebellum as determined by [(3)H]muscimol binding to the immunoprecipitated receptor assemblies. These results indicate that the delta-subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors may play a role in chronic ethanol-induced tolerance and dependence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of chronic administration of ethanol on GABAA receptor assemblies derived from alpha2-, alpha3-, beta2- and gamma2-subunits in the rat cerebral cortex.Brain Res. 2005 Jan 7;1031(1):134-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.11.001. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15621022
-
Low concentrations of ethanol do not affect radioligand binding to the delta-subunit-containing GABAA receptors in the rat brain.Brain Res. 2007 Aug 24;1165:15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.051. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17662260 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of the GABAA receptor assemblies containing alpha1-subunit in the rat cerebellum and cerebral cortex as determined by immunoprecipitation: lack of modulation by chronic ethanol administration.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999 Apr 6;67(1):194-9. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(99)00020-0. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10101248
-
Ethanol regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors: genomic and nongenomic mechanisms.Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Mar;101(3):211-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.12.001. Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15031000 Review.
-
The role of GABA(A) receptors in the acute and chronic effects of ethanol.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1998 Sep;139(1-2):2-19. doi: 10.1007/s002130050685. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1998. PMID: 9768538 Review.
Cited by
-
Daily isoflurane exposure increases barbiturate insensitivity in medullary respiratory and cortical neurons via expression of ε-subunit containing GABA ARs.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 6;10(3):e0119351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119351. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25748028 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-Review: Effects of Ethanol on GABAA Receptor-Mediated Neurotransmission in the Cerebellar Cortex--Recent Advances.Cerebellum. 2015 Aug;14(4):438-46. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0639-3. Cerebellum. 2015. PMID: 25575727 Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of GABAergic Neurotransmission and Neurosteroid Biosynthesis in Alcohol Use Disorder.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Feb 15;24(2):130-141. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa073. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32968808 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine: alcohol reward interactions.Neurochem Res. 2010 Aug;35(8):1248-58. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0181-8. Epub 2010 May 25. Neurochem Res. 2010. PMID: 20499168 Review.
-
After damage of large bile ducts by gamma-aminobutyric acid, small ducts replenish the biliary tree by amplification of calcium-dependent signaling and de novo acquisition of large cholangiocyte phenotypes.Am J Pathol. 2010 Apr;176(4):1790-800. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090677. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20185575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguayo LG, Peoples RW, Yeh HH, Yevenes GE. GABAA receptors as molecular sites of ethanol action. Direct or indirect actions? Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002;2:869–885. - PubMed
-
- Benke D, Mertens S, Trzeciak A, Gillessen D, Mohler H. GABAA receptors display association of γ2-subunit with α1- and β2/3-subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:4478–4483. - PubMed
-
- Bjornstrom K, Sjolander A, Schippert A, Eintrei C. A tyrosine kinase regulates propofol-induced modulation of the β-subunit of the GABAA receptor and release of intracellular calcium in cortical rat neurones. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2002;175:227–235. - PubMed
-
- Borghese CM, Storustovu SI, Ebert B, Herd MB, Belelli D, Lambert JJ, Marshall G, Wafford KA, Harris RA. The δ subunit of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors does not confer sensitivity to low concentrations of ethanol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006;316:1360–1368. - PubMed
-
- Cagetti E, Liang J, Spigelman I, Olsen RW. Withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol treatment changes subunit composition, reduces synaptic function, and decreases behavioral responses to positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003;63:53–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

