Relationship of alcohol consumption and type of alcoholic beverage consumed with plasma lipid levels: differences between Whites and African Americans of the ARIC study
- PMID: 17855114
- PMCID: PMC2819069
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.07.103
Relationship of alcohol consumption and type of alcoholic beverage consumed with plasma lipid levels: differences between Whites and African Americans of the ARIC study
Abstract
Purpose: Alcohol consumption has been shown to contribute to a favorable lipid profile, and most studies have reported a reduction in coronary heart disease risk with low-to-moderate consumption of alcohol that is generally attributed to the beneficial effects of alcohol on lipids. The influence of different types of alcoholic beverages on plasma lipid levels has been investigated to a lesser extent and in limited populations.
Methods: We investigated the effect of overall alcohol consumption, as well as the type of alcoholic beverage consumed, on multiple lipid measures in the large bi-ethnic population of the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study.
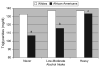
Results: We found both low-to-moderate and heavy alcohol consumption, regardless of the type of alcoholic beverage consumed, to result in significantly greater levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, HDL3 cholesterol, and apolipoprotein A-I in both white and African-American males and females. Associations with other lipid measures contrasted between whites and African Americans, with greater levels of alcohol consumption resulting in significantly greater triglyceride levels in African Americans.
Conclusions: Our results confirm previous studies associating alcohol consumption, regardless of beverage type, with greater HDL cholesterol levels, with additional consistent associations detected for the major HDL cholesterol density subfraction, HDL3 cholesterol, and the major HDL cholesterol structural apolipoprotein, apolipoprotein A-I.
Figures
References
-
- Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Willett WC, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH. A prospective study of moderate alcohol consumption and the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:267–273. - PubMed
-
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Ascherio A, Rosner B, Stampfer MJ. Prospective study of alcohol consumption and risk of coronary disease in men. Lancet. 1991;338:464–468. - PubMed
-
- Camargo CA, Hennekens CH, Gaziano JM, Glynn RJ, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ. Prospective study of moderate alcohol consumption and mortality in US male physicians. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:79–85. - PubMed
-
- Friedman LA, Kimball AW. Coronary heart disease mortality and alcohol consumption in Framingham. Am J Epidemiol. 1986;124:481–489. - PubMed
-
- Renaud SC, Gueguen R, siest G, Salamon R. Wine, beer, and mortality in middle-aged men from Eastern France. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1865–1870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

