Targeting Cre recombinase to specific neuron populations with bacterial artificial chromosome constructs
- PMID: 17855595
- PMCID: PMC6672645
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2707-07.2007
Targeting Cre recombinase to specific neuron populations with bacterial artificial chromosome constructs
Abstract
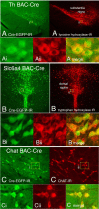
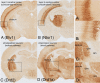
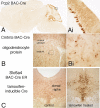
Transgenic mouse lines are characterized with Cre recombinase driven by promoters of CNS-specific genes using bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) constructs. BAC-Cre constructs for 10 genes (Chat, Th, Slc6a4, Slc6a2, Etv1, Ntsr1, Drd2, Drd1, Pcp2, and Cmtm5) produced 14 lines with Cre expression in specific neuronal and glial populations in the brain. These Cre driver lines add functional utility to the >500 BAC-EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) transgenic mouse lines that are part of the Gene Expression Nervous System Atlas Project.
Figures
References
-
- Aller MI, Jones A, Merlo D, Paterlini M, Meyer AH, Amtmann U, Brickley S, Jolin HE, McKenzie AN, Monyer H, Farrant M, Wisden W. Cerebellar granule cell Cre recombinase expression. Genesis. 2003;36:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Branda CS, Dymecki SM. Talking about a revolution: the impact of site-specific recombinases on genetic analyses in mice. Dev Cell. 2004;6:7–28. - PubMed
-
- Day M, Wang Z, Ding J, An X, Ingham CA, Shering AF, Wokosin D, Ilijic E, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Mugnaini E, Deutch AY, Sesack SR, Arbuthnott GW, Surmeier DJ. Selective elimination of glutamatergic synapses on striatopallidal neurons in Parkinson disease models. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Gerfen CR, Engber TM, Mahan LC, Susel Z, Chase TN, Monsma FJ, Sibley DR. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor regulated gene expression of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. Science. 1990;250:1429–1432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
