Impact of image segmentation on high-content screening data quality for SK-BR-3 cells
- PMID: 17868449
- PMCID: PMC2080643
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-340
Impact of image segmentation on high-content screening data quality for SK-BR-3 cells
Abstract
Background: High content screening (HCS) is a powerful method for the exploration of cellular signalling and morphology that is rapidly being adopted in cancer research. HCS uses automated microscopy to collect images of cultured cells. The images are subjected to segmentation algorithms to identify cellular structures and quantitate their morphology, for hundreds to millions of individual cells. However, image analysis may be imperfect, especially for "HCS-unfriendly" cell lines whose morphology is not well handled by current image segmentation algorithms. We asked if segmentation errors were common for a clinically relevant cell line, if such errors had measurable effects on the data, and if HCS data could be improved by automated identification of well-segmented cells.
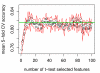
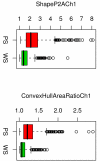
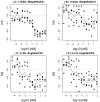
Results: Cases of poor cell body segmentation occurred frequently for the SK-BR-3 cell line. We trained classifiers to identify SK-BR-3 cells that were well segmented. On an independent test set created by human review of cell images, our optimal support-vector machine classifier identified well-segmented cells with 81% accuracy. The dose responses of morphological features were measurably different in well- and poorly-segmented populations. Elimination of the poorly-segmented cell population increased the purity of DNA content distributions, while appropriately retaining biological heterogeneity, and simultaneously increasing our ability to resolve specific morphological changes in perturbed cells.
Conclusion: Image segmentation has a measurable impact on HCS data. The application of a multivariate shape-based filter to identify well-segmented cells improved HCS data quality for an HCS-unfriendly cell line, and could be a valuable post-processing step for some HCS datasets.
Figures






References
-
- Bergman I, Barmada MA, Griffin JA, Slamon DJ. Treatment of meningeal breast cancer xenografts in the rat using an anti-p185/HER2 antibody. Clinical Cancer Research. 2001;7:2050–2056. - PubMed
-
- De Lorenzo C, Palmer DB, Piccoli R, Ritter MA, D'Alessio G. Clinical Cancer Research. Vol. 8. 2002; A new human antitumor immunoreagent specific for ErbB2; pp. 1710–1719. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Yang W, Lan KH, Sellappan S, Klos K, Hortobagyi G, Hung MC, Yu D. Cancer Res. Vol. 62. 2002; Enhanced sensitization to taxol-induced apoptosis by herceptin pretreatment in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells; pp. 5703–5710. - PubMed
-
- Giuliano KA, DeBiasio RL, Dunlay RT, Gough A, Volosky JM, Zock J, Pavlakis GN, Taylor DL. High-Content Screening: A New Approach to Easing Key Bottlenecks in the Drug Discovery Process. J Biomol Screen. 1997;2:249–259. doi: 10.1177/108705719700200410. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

