Do bullae and emphysema increase risk of pneumothorax in silicosis?
- PMID: 17868470
- PMCID: PMC2071907
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6673-2-8
Do bullae and emphysema increase risk of pneumothorax in silicosis?
Abstract
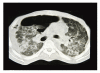
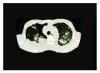
Background: The occurrence of occupational lung diseases is decreasing due to improvements in occupational health in recent years; however, silicosis and its complications remain important occupational health problems. We have studied the role of emphysema and bullae as predictive factors of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax in acute and accelerated silicosis.
Methods: This study was carried out using questionnaire items on occupational history and conventional computed tomography of lungs. Differences between two groups (silicosis with and without secondary spontaneous pneumothorax) in terms of age, interval of exposure-diagnosis and therefore silica exposure duration were assessed by independent t-test. Fisher's exact test was used to determine the association between secondary spontaneous pneumothorax and both emphysema and bullae.
Results: We found a significant association between secondary spontaneous pneumothorax and bullae in acute and accelerated silicosis.
Conclusion: Pneumothorax in silicosis could be attributed to previous bullae.
Figures
References
-
- Strobel SL. Pathologic quiz case: Recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax in an industrial worker. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126:749–750. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qudah A. Treatment options of spontaneous pneumothorax. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006;48:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Weill H, Jones RN, Parkes WR. Silicosis and related diseases. In: Parkes WR, editor. Occupational Lung Disorders. 3. Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1994. pp. 285–339.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

