The regulation of myosin binding to actin filaments by Lethocerus troponin
- PMID: 17868693
- PMCID: PMC2238177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.066
The regulation of myosin binding to actin filaments by Lethocerus troponin
Abstract
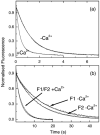
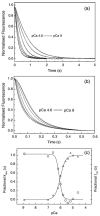
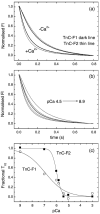
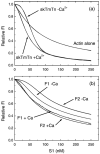
Lethocerus indirect flight muscle has two isoforms of troponin C, TnC-F1 and F2, which are unusual in having only a single C-terminal calcium binding site (site IV, isoform F1) or one C-terminal and one N-terminal site (sites IV and II, isoform F2). We show here that thin filaments assembled from rabbit actin and Lethocerus tropomyosin (Tm) and troponin (Tn) regulate the binding of rabbit myosin to rabbit actin in much the same way as the mammalian regulatory proteins. The removal of calcium reduces the rate constant for S1 binding to regulated actin about threefold, independent of which TmTn is used. This is consistent with calcium removal causing the TmTn to occupy the B or blocked state to about 70% of the total. The mid point pCa for the switch differed for TnC-F1 and F2 (pCa 6.9 and 6.0, respectively) consistent with the reported calcium affinities for the two TnCs. Equilibrium titration of S1 binding to regulated actin filaments confirms calcium regulated binding of S1 to actin and shows that in the absence of calcium the three actin filaments (TnC-F1, TnC-F2 and mammalian control) are almost indistinguishable in terms of occupancy of the B and C states of the filament. In the presence of calcium TnC-F2 is very similar to the control with approximately 80% of the filament in the C-state and 10-15% in the fully on M-State while TnC-F1 has almost 50% in each of the C and M states. This higher occupancy of the M-state for TnC-F1, which occurs above pCa 6.9, is consistent with this isoform being involved in the calcium activation of stretch activation. However, it leaves unanswered how a C-terminal calcium binding site of TnC can activate the thin filament.
Figures

References
-
- Pringle J. Stretch activation of muscle: function and mechanism. Proc. Roy. Soc. ser. B. 1978;201:107–130. - PubMed
-
- Josephson RK, Malamud JG, Stokes DR. Asynchronous muscle: a primer. J. Exp. Biol. 2000;203:2713–2722. - PubMed
-
- Esch H, Goller F, Heinrich B. How do bees shiver? Naturwissenschaften. 1991;78:325–328. - PubMed
-
- Heinrich B. The Thermal Warriors: Strategies of Insect Survival. Harvard University Press; Cambridge, MA: 1996.
-
- Kuhn HJ, Bletz C, Guth K, Ruegg JC. The effect of MgATP on forming and breaking actin-myosin linkages in contracted skinned insect flight muscle fibres. J. Mus. Res. Cell Motil. 1985;6:5–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

