Extensive mutagenesis experiments corroborate a structural model for the DNA deaminase domain of APOBEC3G
- PMID: 17869248
- PMCID: PMC2014798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.08.076
Extensive mutagenesis experiments corroborate a structural model for the DNA deaminase domain of APOBEC3G
Abstract
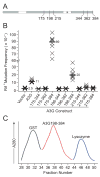
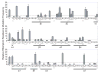
APOBEC3G is a single-strand DNA cytosine deaminase capable of blocking retrovirus and retrotransposon replication. APOBEC3G has two conserved zinc-coordinating motifs but only one is required for catalysis. Here, deletion analyses revealed that the minimal catalytic domain consists of residues 198-384. Size exclusion assays indicated that this protein is monomeric. Many (31/69) alanine substitution derivatives of APOBEC3G198-384 retained significant to full levels of activity. These data corroborated an APOBEC2-based structural model for the catalytic domain of APOBEC3G indicating that most non-essential residues are solvent accessible and most essential residues cluster within the protein core.
Figures


References
-
- Longerich S, Basu U, Alt F, Storb U. AID in somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:164–74. - PubMed
-
- Sheehy AM, Gaddis NC, Choi JD, Malim MH. Isolation of a human gene that inhibits HIV-1 infection and is suppressed by the viral Vif protein. Nature. 2002;418:646–50. - PubMed
-
- Harris RS, Petersen-Mahrt SK, Neuberger MS. RNA editing enzyme APOBEC1 and some of its homologs can act as DNA mutators. Molecular Cell. 2002;10:1247–53. - PubMed
-
- Harris RS, Bishop KN, Sheehy AM, Craig HM, Petersen-Mahrt SK, Watt IN, Neuberger MS, Malim MH. DNA deamination mediates innate immunity to retroviral infection. Cell. 2003;113:803–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

