A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model
- PMID: 17870179
- PMCID: PMC2259391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.08.004
A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model
Abstract
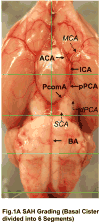
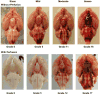
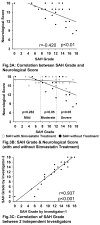
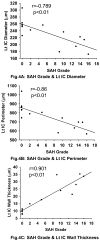
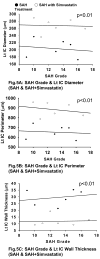
The endovascular perforation rodent model for experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) studies is criticized for lack of control over bleeding. Presently, there is no practical grading system to categorize the severity of SAH depending on the amount of blood. We outline a simple and objective novel SAH grading system by examining the subarachnoid blood clots in the basal cisterns, and evaluate for correlation with neurological status and cerebral vasospasm. Effects of simvastatin, known to reduce vasospasm, were examined using this grading system. Seventy-seven adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided randomly into three groups: sham-operated (n=24), SAH (n=32), and SAH+simvastatin (n=25). High-resolution brain pictures were used to grade the severity of SAH and categorize animals into mild, moderate and severe groups. The SAH grades were compared with neurological scores and internal carotid artery parameters such as diameter, perimeter and wall thickness at 24h. Two investigators verified the grading system independently. The SAH grade showed linear correlation functionally with neurological status (r=0.42, p<0.01) and morphometrically with the degree of vasospasm (|r|>0.7, p<0.01), and also between two independent investigators (r=0.937, p<0.001). Simvastatin improved neurological score in moderate and severe (p<0.05) but not mild SAH groups (p=0.28). This grading system has the potential to be adopted for SAH experimental rodent models.
Figures

References
-
- Aladag MA, Turkoz Y, Ozcan C, Sahna E, Parlakpinar H, Akpolat N, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) attenuates cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoidal haemorrhage by increasing brain nitric oxide levels. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2006;24:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Germano IM, Guarino L. Cortical blood flow and cerebral perfusion pressure in a new noncraniotomy model of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke. 1995;26:1086–1091. - PubMed
-
- Cahill J, Calvert JW, Solaroglu I, Zhang JH. Vasospasm and p53-induced apoptosis in an experimental model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2006;37:1868–1874. - PubMed
-
- Cimino M, Balduini W, Carloni S, Gelosa P, Guerrini U, Tremoli E, et al. Neuroprotective effect of simvastatin in stroke: a comparison between adult and neonatal rat models of cerebral ischemia. Neurotoxicology. 2005;26:929–933. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation Stroke. 1995;26:627–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

