Structural basis of viral invasion: lessons from paramyxovirus F
- PMID: 17870467
- PMCID: PMC2086805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.08.016
Structural basis of viral invasion: lessons from paramyxovirus F
Abstract
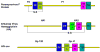
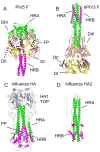
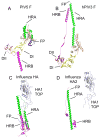
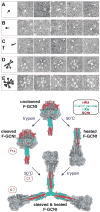
The structures of glycoproteins that mediate enveloped virus entry into cells have revealed dramatic structural changes that accompany membrane fusion and provided mechanistic insights into this process. The group of class I viral fusion proteins includes the influenza hemagglutinin, paramyxovirus F, HIV env, and other mechanistically related fusogens, but these proteins are unrelated in sequence and exhibit clearly distinct structural features. Recently determined crystal structures of the paramyxovirus F protein in two conformations, representing pre-fusion and post-fusion states, reveal a novel protein architecture that undergoes large-scale, irreversible refolding during membrane fusion, extending our understanding of this diverse group of membrane fusion machines.
Figures

References
-
- Harrison SC. Principles of Virus Structure. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 5. Vol. 1 Wolters Kluwer: Lippincott WIlliams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 59–98.
-
- Helenius A. Virus Entry and Uncoating. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. Vol. 1 Wolters Kluwer: Lippincott WIlliams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 99–118.
-
- Wilson IA, Skehel JJ, Wiley DC. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 Å resolution. Nature. 1981;289:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Bullough PA, Hughson FM, Skehel JJ, Wiley DC. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994;371:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Skehel JJ, Wiley DC. Receptor binding and membrane fusion in virus entry: the influenza hemagglutinin. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:531–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

