Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs
- PMID: 17872505
- PMCID: PMC2040081
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.768207
Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs
Abstract
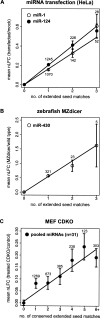
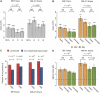
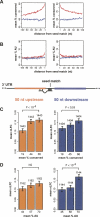
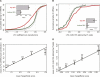
Vertebrate mRNAs are frequently targeted for post-transcriptional repression by microRNAs (miRNAs) through mechanisms involving pairing of 3' UTR seed matches to bases at the 5' end of miRNAs. Through analysis of expression array data following miRNA or siRNA overexpression or inhibition, we found that mRNA fold change increases multiplicatively (i.e., log-additively) with seed match count and that a single 8 mer seed match mediates down-regulation comparable to two 7 mer seed matches. We identified several targeting determinants that enhance seed match-associated mRNA repression, including the presence of adenosine opposite miRNA base 1 and of adenosine or uridine opposite miRNA base 9, independent of complementarity to the siRNA/miRNA. Increased sequence conservation in the approximately 50 bases 5' and 3' of the seed match and increased AU content 3' of the seed match were each independently associated with increased mRNA down-regulation. All of these determinants are enriched in the vicinity of conserved miRNA seed matches, supporting their activity in endogenous miRNA targeting. Together, our results enable improved siRNA off-target prediction, allow integrated ranking of conserved and nonconserved miRNA targets, and show that targeting by endogenous and exogenous miRNAs/siRNAs involves similar or identical determinants.
Figures
References
-
- Abbondanzo, S.J., Gadi, I., Stewart, C.L. Derivation of embryonic stem cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:803–823. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bagga, S., Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Massirer, K., Holtz, J., Eachus, R., Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
