The Escherichia coli Yej transporter is required for the uptake of translation inhibitor microcin C
- PMID: 17873039
- PMCID: PMC2168686
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01028-07
The Escherichia coli Yej transporter is required for the uptake of translation inhibitor microcin C
Abstract
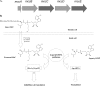
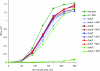
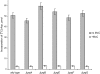
Microcin C (McC), a peptide-nucleotide antibiotic, targets aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. By analyzing a random transposon library, we identified Escherichia coli mutants resistant to McC. Transposon insertions were localized to a single locus, yejABEF, which encodes components of a putative inner membrane ABC transporter. Analysis of site-specific mutants established that all four components of the transporter are required for McC sensitivity. Since aspartyl-tRNA synthetase in yej mutant extracts was fully sensitive to McC, we conclude that yej mutations interfere with McC uptake and that YejABEF is the only inner membrane transporter responsible for McC uptake in E. coli. Other substrates of YejABEF remain to be identified.
Figures

References
-
- Baquero, F., and F. Moreno. 1984. The microcins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 23:117-124.
-
- Braun, V., S. I. Patzer, and K. Hantke. 2002. Ton-dependent colicins and microcins: modular design and evolution. Biochimie 84:365-380. - PubMed
-
- Chiang, S. L., and E. J. Rubin. 2002. Construction of a mariner-based transposon for epitope-tagging and genomic targeting. Gene 296:179-185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

