In vivo DNA binding of bacteriophage GA-1 protein p6
- PMID: 17873040
- PMCID: PMC2168694
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01047-07
In vivo DNA binding of bacteriophage GA-1 protein p6
Abstract
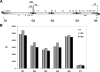
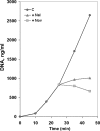
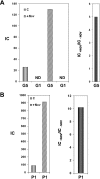
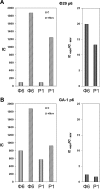
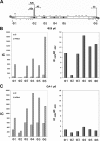
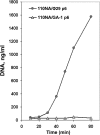
Bacteriophage GA-1 infects Bacillus sp. strain G1R and has a linear double-stranded DNA genome with a terminal protein covalently linked to its 5' ends. GA-1 protein p6 is very abundant in infected cells and binds DNA with no sequence specificity. We show here that it binds in vivo to the whole viral genome, as detected by cross-linking, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and real-time PCR analyses, and has the characteristics of a histone-like protein. Binding to DNA of GA-1 protein p6 shows little supercoiling dependency, in contrast to the ortholog protein of the evolutionary related Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. This feature is a property of the protein rather than the DNA or the cellular background, since phi29 protein p6 shows supercoiling-dependent binding to GA-1 DNA in Bacillus sp. strain G1R. GA-1 DNA replication is impaired in the presence of the gyrase inhibitors novobiocin and nalidixic acid, which indicates that, although noncovalently closed, the viral genome is topologically constrained in vivo. GA-1 protein p6 is also able to bind phi29 DNA in B. subtilis cells; however, as expected, the binding is less supercoiling dependent than the one observed with the phi29 protein p6. In addition, the nucleoprotein complex formed is not functional, since it is not able to transcomplement the DNA replication deficiency of a phi29 sus6 mutant. Furthermore, we took advantage of phi29 protein p6 binding to GA-1 DNA to find that the viral DNA ejection mechanism seems to take place, as in the case of phi29, with a right to left polarity in a two-step, push-pull process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phage phi29 proteins p1 and p17 are required for efficient binding of architectural protein p6 to viral DNA in vivo.J Bacteriol. 2004 Dec;186(24):8401-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.24.8401-8406.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15576790 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide, supercoiling-dependent in vivo binding of a viral protein involved in DNA replication and transcriptional control.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Apr 26;32(8):2306-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh565. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15118076 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of phage Phi29 architectural protein p6 to the viral genome: evidence for topological restriction of the phage linear DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 1;32(11):3493-502. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh668. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15247336 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage Ø29 protein p6: an architectural protein involved in genome organization, replication and control of transcription.J Mol Recognit. 2004 Sep-Oct;17(5):390-6. doi: 10.1002/jmr.701. J Mol Recognit. 2004. PMID: 15362097 Review.
-
DNA structure in the nucleoprotein complex that activates replication of phage phi 29.Biophys Chem. 1994 May;50(1-2):183-9. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)85030-5. Biophys Chem. 1994. PMID: 8011933 Review.
Cited by
-
Flexible structural arrangement and DNA-binding properties of protein p6 from Bacillus subtillis phage φ29.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):2045-2065. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae041. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38281216 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-Binding Proteins Essential for Protein-Primed Bacteriophage Φ29 DNA Replication.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Aug 5;3:37. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00037. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27547754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Landscape of Phenotypic and Transcriptional Responses to Ciprofloxacin in Acinetobacter baumannii: Acquired Resistance Alleles Modulate Drug-Induced SOS Response and Prophage Replication.mBio. 2019 Jun 11;10(3):e01127-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01127-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31186328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abril, A. M., S. Marco, J. L. Carrascosa, M. Salas, and J. M. Hermoso. 1999. Oligomeric structures of the phage φ29 histone-like protein p6. J. Mol. Biol. 292:581-588. - PubMed
-
- Abril, A. M., M. Salas, J. M. Andreu, J. M. Hermoso, and G. Rivas. 1997. Phage φ29 protein p6 is in a monomer-dimer equilibrium that shifts to higher association states at the millimolar concentrations found in vivo. Biochemistry 36:11901-11908. - PubMed
-
- Barthelemy, I., and M. Salas. 1989. Characterization of a new prokaryotic transcriptional activator and its DNA recognition site. J. Mol. Biol. 208:225-232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

