Dual role of the plastid terminal oxidase in tomato
- PMID: 17873087
- PMCID: PMC2048786
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.106336
Dual role of the plastid terminal oxidase in tomato
Abstract
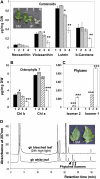
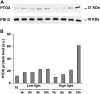
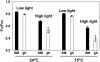
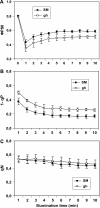
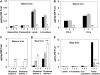
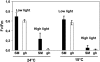
The plastid terminal oxidase (PTOX) is a plastoquinol oxidase whose absence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) results in the ghost (gh) phenotype characterized by variegated leaves (with green and bleached sectors) and by carotenoid-deficient ripe fruit. We show that PTOX deficiency leads to photobleaching in cotyledons exposed to high light primarily as a consequence of reduced ability to synthesize carotenoids in the gh mutant, which is consistent with the known role of PTOX as a phytoene desaturase cofactor. In contrast, when entirely green adult leaves from gh were produced and submitted to photobleaching high light conditions, no evidence for a deficiency in carotenoid biosynthesis was obtained. Rather, consistent evidence indicates that the absence of PTOX renders the tomato leaf photosynthetic apparatus more sensitive to light via a disturbance of the plastoquinone redox status. Although gh fruit are normally bleached (most likely as a consequence of a deficiency in carotenoid biosynthesis at an early developmental stage), green adult fruit could be obtained and submitted to photobleaching high light conditions. Again, our data suggest a role of PTOX in the regulation of photosynthetic electron transport in adult green fruit, rather than a role principally devoted to carotenoid biosynthesis. In contrast, ripening fruit are primarily dependent on PTOX and on plastid integrity for carotenoid desaturation. In summary, our data show a dual role for PTOX. Its activity is necessary for efficient carotenoid desaturation in some organs at some developmental stages, but not all, suggesting the existence of a PTOX-independent pathway for plastoquinol reoxidation in association with phytoene desaturase. As a second role, PTOX is implicated in a chlororespiratory mechanism in green tissues.
Figures



References
-
- Aluru MR, Stessman DJ, Spalding MH, Rodermel SR (2007) Alterations in photosynthesis in Arabidopsis lacking IMMUTANS, a chloroplast terminal oxidase. Photosynth Res 91 11–23 - PubMed
-
- Aluru MR, Yu F, Fu A, Rodermel S (2006) Arabidopsis variegation mutants: new insights into chloroplast biogenesis. J Exp Bot 57 1871–1881 - PubMed
-
- Baena-Gonzalez E, Allahverdiyeva Y, Svab Z, Maliga P, Josse EM, Kuntz M, Maenpaa P, Aro EM (2003) Deletion of the tobacco plastid psbA gene triggers an upregulation of the thylakoid-associated NAD(P)H dehydrogenase complex and the plastid terminal oxidase (PTOX). Plant J 35 704–716 - PubMed
-
- Baerr JN, Thomas JD, Taylor BG, Rodermel SR, Gray GR (2005) Differential photosynthetic compensatory mechanisms exist in the immutans mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol Plant 124 390–402
-
- Barr J, White WS, Chen L, Bae CH, Rodermel S (2004) The GHOST terminal oxidase regulates developmental programming in tomato fruit. Plant Cell Environ 27 840–852
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

