Vitamer levels, stress response, enzyme activity, and gene regulation of Arabidopsis lines mutant in the pyridoxine/pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase (PDX3) and the pyridoxal kinase (SOS4) genes involved in the vitamin B6 salvage pathway
- PMID: 17873088
- PMCID: PMC2048783
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.105189
Vitamer levels, stress response, enzyme activity, and gene regulation of Arabidopsis lines mutant in the pyridoxine/pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase (PDX3) and the pyridoxal kinase (SOS4) genes involved in the vitamin B6 salvage pathway
Abstract
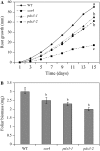
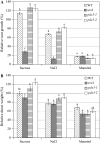
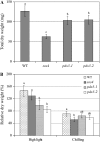
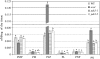
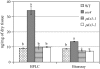
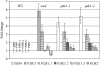
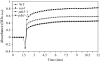
PDX3 and SALT OVERLY SENSITIVE4 (SOS4), encoding pyridoxine/pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase and pyridoxal kinase, respectively, are the only known genes involved in the salvage pathway of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate in plants. In this study, we determined the phenotype, stress responses, vitamer levels, and regulation of the vitamin B(6) pathway genes in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) plants mutant in PDX3 and SOS4. sos4 mutant plants showed a distinct phenotype characterized by chlorosis and reduced plant size, as well as hypersensitivity to sucrose in addition to the previously noted NaCl sensitivity. This mutant had higher levels of pyridoxine, pyridoxamine, and pyridoxal 5'-phosphate than the wild type, reflected in an increase in total vitamin B(6) observed through HPLC analysis and yeast bioassay. The sos4 mutant showed increased activity of PDX3 as well as of the B(6) de novo pathway enzyme PDX1, correlating with increased total B(6) levels. Two independent lines with T-DNA insertions in the promoter region of PDX3 (pdx3-1 and pdx3-2) had decreased PDX3 activity. Both also had decreased activity of PDX1, which correlated with lower levels of total vitamin B(6) observed using the yeast bioassay; however, no differences were noted in levels of individual vitamers by HPLC analysis. Both pdx3 mutants showed growth reduction in vitro and in vivo as well as an inability to increase growth under high light conditions. Increased expression of salvage and some of the de novo pathway genes was observed in both the pdx3 and sos4 mutants. In all mutants, increased expression was more dramatic for the salvage pathway genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Balancing of B6 Vitamers Is Essential for Plant Development and Metabolism in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Feb;28(2):439-53. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.01033. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 26858304 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a pyridoxal reductase involved in the vitamin B6 salvage pathway in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 May;76(1-2):157-69. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9777-x. Epub 2011 May 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21533842
-
The Arabidopsis salt overly sensitive 4 mutants uncover a critical role for vitamin B6 in plant salt tolerance.Plant Cell. 2002 Mar;14(3):575-88. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010417. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 11910005 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin B(6) salvage enzymes: mechanism, structure and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1814(11):1597-608. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.12.006. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21182989 Review.
-
Update on interconversions of vitamin B-6 with its coenzyme.J Nutr. 1999 Feb;129(2):325-7. doi: 10.1093/jn/129.2.325. J Nutr. 1999. PMID: 10024608 Review.
Cited by
-
The Arabidopsis splicing regulator SR45 confers salt tolerance in a splice isoform-dependent manner.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jul;100(4-5):379-390. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00864-4. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30968308
-
Balancing of B6 Vitamers Is Essential for Plant Development and Metabolism in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Feb;28(2):439-53. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.01033. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 26858304 Free PMC article.
-
Pyridoxal phosphate synthases PdxS/PdxT are required for Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae viability, stress tolerance and virulence.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 27;12(4):e0176374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176374. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28448619 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of indole-3-acetic acid photodegradation by vitamin B6.Mol Plant. 2013 Nov;6(6):1992-5. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst089. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23723155 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Phosphorylated B6 vitamer deficiency in SALT OVERLY SENSITIVE 4 mutants compromises shoot and root development.Plant Physiol. 2022 Jan 20;188(1):220-240. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab475. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34730814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanove AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Argoudelis CJ (1999) Identification of the vitamers of vitamin B6 excreted by a yeast mutant growing in a glucose minimal culture medium. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 721 21–29 - PubMed
-
- Burns KE, Xiang Y, Kinsland CL, McLafferty FW, Begley TP (2005) Reconstitution and biochemical characterization of a new pyridoxal-5′-phosphate biosynthetic pathway. J Am Chem Soc 127 3682–3683 - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Xiong L (2005) Pyridoxine is required for post-embryonic root development and tolerance to osmotic and oxidative stress. Plant J 44 396–408 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

