High proportion of large genomic deletions and a genotype phenotype update in 80 unrelated families with juvenile polyposis syndrome
- PMID: 17873119
- PMCID: PMC2752176
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2007.052506
High proportion of large genomic deletions and a genotype phenotype update in 80 unrelated families with juvenile polyposis syndrome
Abstract
Background: In patients with juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) the frequency of large genomic deletions in the SMAD4 and BMPR1A genes was unknown.
Methods: Mutation and phenotype analysis was used in 80 unrelated patients of whom 65 met the clinical criteria for JPS (typical JPS) and 15 were suspected to have JPS.
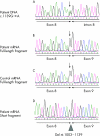
Results: By direct sequencing of the two genes, point mutations were identified in 30 patients (46% of typical JPS). Using MLPA, large genomic deletions were found in 14% of all patients with typical JPS (six deletions in SMAD4 and three deletions in BMPR1A). Mutation analysis of the PTEN gene in the remaining 41 mutation negative cases uncovered a point mutation in two patients (5%). SMAD4 mutation carriers had a significantly higher frequency of gastric polyposis (73%) than did patients with BMPR1A mutations (8%) (p<0.001); all seven cases of gastric cancer occurred in families with SMAD4 mutations. SMAD4 mutation carriers with gastric polyps were significantly older at gastroscopy than those without (p<0.001). In 22% of the 23 unrelated SMAD4 mutation carriers, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) was also diagnosed clinically. The documented histologic findings encompassed a wide distribution of different polyp types, comparable with that described in hereditary mixed polyposis syndromes (HMPS).
Conclusions: Screening for large deletions raised the mutation detection rate to 60% in the 65 patients with typical JPS. A strong genotype-phenotype correlation for gastric polyposis, gastric cancer, and HHT was identified, which should have implications for counselling and surveillance. Histopathological results in hamartomatous polyposis syndromes must be critically interpreted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Haidle J L, Howe J R. Juvenile polyposis syndrome. http://www.genetests.org (accessed 22 February 2007)
-
- Chow E, Macrae F. A review of juvenile polyposis syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005201634–1640. - PubMed
-
- Howe J R, Roth S, Ringold J C, Summers R W, Jarvinen H J, Sistonen P, Tomlinson I P, Houlston R S, Bevan S, Mitros F A, Stone E M, Aaltonen L A. Mutations in the SMAD4/DPC4 gene in juvenile polyposis. Science 19982801086–1088. - PubMed
-
- Howe J R, Bair J L, Sayed M G, Anderson M E, Mitros F A, Petersen G M, Velculescu V E, Traverso G, Vogelstein B. Germline mutations of the gene encoding bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1A in juvenile polyposis. Nat Genet 200128184–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous