Phenolic compounds and antimicrobial activity of olive (Olea europaea L. Cv. Cobrançosa) leaves
- PMID: 17873849
- PMCID: PMC6149345
- DOI: 10.3390/12051153
Phenolic compounds and antimicrobial activity of olive (Olea europaea L. Cv. Cobrançosa) leaves
Abstract
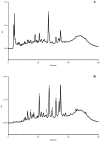
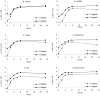
We report the determination of phenolic compounds in olive leaves by reversed-phase HPLC/DAD, and the evaluation of their in vitro activity against several microorganisms that may be causal agents of human intestinal and respiratory tract infections, namely gram positive (Bacillus cereus, B. subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus), gram negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae) and fungi (Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans). Seven phenolic compounds were identified and quantified: caffeic acid, verbascoside, oleuropein, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, rutin, apigenin 7-O-glucoside and luteolin 4'-O-glucoside. At low concentrations olive leaves extracts showed an unusual combined antibacterial and antifungal action, which suggest their great potential as nutraceuticals, particularly as a source of phenolic compounds.
Figures
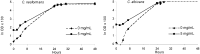
References
-
- Guinda A., Albi T., Camino M. C. P., Lanzón A. Supplementation of oils with oleanolic acid from the olive leaf (Olea europaea) Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004;106:22–26. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200300769. - DOI
-
- Tabera J., Guinda A., Ruiz-Rodriguez A., Senorans J. F., Ibanez E., Albi T., Reglero G. Countercurrent supercritical fluid extraction and fractionation of high-added-value compounds from a hexane extract of olive leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004;52:4774–4779. - PubMed
-
- Samuelsson G. The blood pressure lowering factor in leaves of Olea europaea. Farmacevtisk Revy. 1951;15:229–239.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

