Not your parents' test scores: cohort reduces psychometric aging effects
- PMID: 17874953
- PMCID: PMC4169292
- DOI: 10.1037/0882-7974.22.3.546
Not your parents' test scores: cohort reduces psychometric aging effects
Abstract
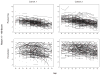
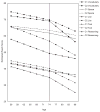
Increases over birth cohorts in psychometric abilities may impact effects of aging. Data from 2 cohorts of the Long Beach Longitudinal Study, matched on age but tested 16 years apart, were modeled over ages 55-87 to test the hypothesis that the more fluid abilities of reasoning, list and text recall, and space would show larger cohort differences than vocabulary. This hypothesis was confirmed. At age 74, average performance estimates for people from the more recently born cohort were equivalent to those of people from the older cohort when they were up to 15 years younger. This finding suggests that older adults may perform like much younger ones from the previous generation on fluid measures, indicating higher levels of abilities than expected. This result could have major implications for the expected productivity of an aging workforce as well as for the quality of life of future generations. However, cohort improvements did not mitigate age declines.
(PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2007 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Examining the interaction of age x race pertaining to black-white differences at ages 15 to 93 on six Horn abilities assessed by K-FAST, K-SNAP, and KAIT subtests.Percept Mot Skills. 1994 Dec;79(3 Pt 2):1683-90. doi: 10.2466/pms.1994.79.3f.1683. Percept Mot Skills. 1994. PMID: 7870562
-
Relationship between rigidity-flexibility and cognitive abilities in adulthood.Psychol Aging. 1991 Sep;6(3):371-83. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.6.3.371. Psychol Aging. 1991. PMID: 1930754
-
Sixteen-year longitudinal and time lag changes in memory and cognition in older adults.Psychol Aging. 1997 Sep;12(3):503-13. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.12.3.503. Psychol Aging. 1997. PMID: 9308097
-
The cognitive reserve hypothesis: a longitudinal examination of age-associated declines in reasoning and processing speed.Dev Psychol. 2009 Mar;45(2):431-46. doi: 10.1037/a0014012. Dev Psychol. 2009. PMID: 19271829 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Stability and change in cognitive ability over the life span: a comparison of populations with and without Down's syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2005 Dec;49(Pt 12):915-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00735.x. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2005. PMID: 16287480 Review.
Cited by
-
Secular trends in cognitive trajectories of diverse older adults.Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Dec;15(12):1576-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.06.4944. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. PMID: 31672483 Free PMC article.
-
How Interventions Might Improve Cognition in Healthy Older Adults.Int J Gaming Comput Mediat Simul. 2013;5(3):72-82. doi: 10.4018/jgcms.2013070105. Int J Gaming Comput Mediat Simul. 2013. PMID: 33329761 Free PMC article.
-
The Flynn effect and cognitive decline among americans aged 65 years and older.Psychol Aging. 2024 Aug;39(5):457-466. doi: 10.1037/pag0000833. Psychol Aging. 2024. PMID: 39052350 Free PMC article.
-
Reading Comprehension in Older Adults-Effects of Age, Educational Level, and Reading Habits.J Intell. 2024 Dec 31;13(1):4. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence13010004. J Intell. 2024. PMID: 39852413 Free PMC article.
-
The association between higher order abilities, processing speed, and age are variably mediated by white matter integrity during typical aging.Neuropsychologia. 2013 Jul;51(8):1435-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Neuropsychologia. 2013. PMID: 23507612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike H. Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika. 1987;52:317–332.
-
- Alwin DF. Family of origin and cohort differences in verbal ability. American Sociological Review. 1991;56:625–638.
-
- Alwin DF, McCammon RJ. Aging, cohorts, and verbal ability. Journals of Gerontology, Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. 2001;56:S151–S161. - PubMed
-
- Barber N. Educational and ecological correlates of IQ: A cross-national investigation. Intelligence. 2005;33:273–284.
-
- Blair C, Gamson D, Thorne S, Baker D. Rising mean IQ: Cognitive demand of mathematics education for young children, population exposure to formal schooling, and the neurobiology of the pre-frontal cortex. Intelligence. 2005;33:93–106.

