Sublingual administration of furosemide: new application of an old drug
- PMID: 17875188
- PMCID: PMC2198789
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03035.x
Sublingual administration of furosemide: new application of an old drug
Abstract
Background: In patients with decompensated heart failure, absorption of orally administered furosemide may be delayed, possibly leading to impaired pharmacodynamic effects. Sublingual administration may represent an alternative in such situations.
Methods: In a crossover study including 11 healthy men, 20 mg furosemide was administered intravenously, orally and sublingually on three different days. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics were assessed from repeated blood and urine samples.
Results: Compared with oral administration, sublingual administration was associated with 43% higher C(max)[difference 215 ng ml(-1), 95% confidence interval (CI) 37, 392], a higher urinary recovery (8.9 vs. 7.3 mg, difference 1.6 mg, 95% CI 0.3, 2.9), an 28% higher AUC (difference 328 ng h(-1) ml(-1), 95% CI 24, 632) and a higher bioavailability of furosemide (59 vs. 47%, difference 12.0%, 95% CI -1.2, 25.2). Sodium excretion was higher after sublingual compared with oral administration (peak excretion rate 1.8 vs. 1.4 mmol min(-1), P < 0.05), whereas urine volume did not differ significantly between the two application modes. In comparison, intravenous administration showed the expected more rapid and intense response.
Conclusion: Sublingually administered furosemide tablets differ in certain kinetic and dynamic properties from identical tablets given orally. Sublingual administration of furosemide may offer therapeutic advantages in certain groups of patients.
Figures
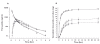
 ); sublingual, (
); sublingual, ( )
)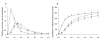
 ); sublingual, (
); sublingual, ( ); intravenous, (○)
); intravenous, (○)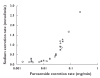
 ); sublingual, (
); sublingual, ( )
)
 ); sublingual, (
); sublingual, ( ); intravenous, (○)
); intravenous, (○)References
-
- Swedberg K, Cleland J, Dargie H, Drexler H, Follath F, Komajda M, Tavazzi L, Smiseth OA, Gavazzi A, Haverich A, Hoes A, Jaarsma T, Korewicki J, Levy S, Linde C, Lopez-Sendon JL, Nieminen MS, Pierard L, Remme WJ. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic heart failure: executive summary (update 2005). The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:1115–40. - PubMed
-
- Brater DC. Resistance to loop diuretics. Why it happens and what to do about it. Drugs. 1985;30:427–43. - PubMed
-
- Brater DC, Day B, Burdette A, Anderson S. Bumetanide and furosemide in heart failure. Kidney Int. 1984;26:183–9. - PubMed
-
- Brater DC, Seiwell R, Anderson S, Burdette A, Dehmer GJ, Chennavasin P. Absorption and disposition of furosemide in congestive heart failure. Kidney Int. 1982;22:171–6. - PubMed
-
- Vargo DL, Kramer WG, Black PK, Smith WB, Serpas T, Brater DC. Bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of torsemide and furosemide in patients with congestive heart failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1995;57:601–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

