Ntr1 activates the Prp43 helicase to trigger release of lariat-intron from the spliceosome
- PMID: 17875666
- PMCID: PMC1973145
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1580507
Ntr1 activates the Prp43 helicase to trigger release of lariat-intron from the spliceosome
Abstract
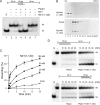
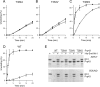
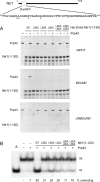
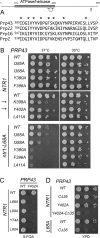
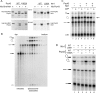
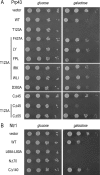
DEAD/H-box NTPases remodel the spliceosome at multiple steps during the pre-mRNA splicing cycle. The RNA-dependent NTPase Prp43 catalyzes dissociation of excised lariat-intron from the spliceosome, but it is unclear how Prp43 couples the energy of ATP hydrolysis to intron release. Here, we report that activation of Prp43's inherently feeble helicase activity by the splicing factor Ntr1 is required for lariat-intron release. Lethal Prp43 mutants T384A and T384V, which are active for ATP hydrolysis and fail to dissociate lariat-intron from spliceosomes, are refractory to stimulation of RNA unwinding by Ntr1. An N-terminal 120-amino-acid segment of Ntr1 suffices for binding to Prp43 and for stimulating its helicase activity. We identify missense mutations in Prp43 and Ntr1 that disrupt protein-protein interaction and impair Ntr1 enhancement of Prp43 RNA unwinding. Our results demonstrate for the first time that regulating the motor activity of a DEAH-box protein by an accessory factor is critical for mRNA splicing.
Figures

References
-
- Aravind L., Koonin E.V., Koonin E.V. G-patch: A new conserved domain in eukaryotic RNA-processing proteins and type D retroviral polyproteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999;24:342–344. - PubMed
-
- Behzadnia N., Golas M.M., Hartmuth K., Sander B., Kastner B., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Golas M.M., Hartmuth K., Sander B., Kastner B., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Hartmuth K., Sander B., Kastner B., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Sander B., Kastner B., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Kastner B., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Deckert J., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Dube P., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Will C.L., Urlaub H., Stark H., Urlaub H., Stark H., Stark H., et al. Composition and three-dimensional EM structure of double affinity-purified, human prespliceosomal A complexes. EMBO J. 2007;26:1737–1748. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boon K.L., Auchynnikava T., Edwalds-Gilbert G., Barrass J.D., Droop A.P., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Auchynnikava T., Edwalds-Gilbert G., Barrass J.D., Droop A.P., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Edwalds-Gilbert G., Barrass J.D., Droop A.P., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Barrass J.D., Droop A.P., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Droop A.P., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Dez C., Beggs J.D., Beggs J.D. Yeast ntr1/spp382 mediates prp43 function in postspliceosomes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006;26:6016–6023. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
