Mechanisms of eosinophil secretion: large vesiculotubular carriers mediate transport and release of granule-derived cytokines and other proteins
- PMID: 17875811
- PMCID: PMC2734949
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0707503
Mechanisms of eosinophil secretion: large vesiculotubular carriers mediate transport and release of granule-derived cytokines and other proteins
Abstract
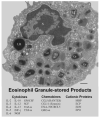
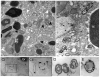
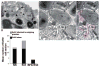
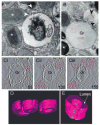
Eosinophils generate and store a battery of proteins, including classical cationic proteins, cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Rapid secretion of these active mediators by eosinophils is central to a range of inflammatory and immunoregulatory responses. Eosinophil products are packaged within a dominant population of cytoplasmic specific granules and generally secreted by piecemeal degranulation, a process mediated by transport vesicles. Large, pleiomorphic vesiculotubular carriers were identified recently as key players for moving eosinophil proteins from granules to the plasma membrane for extracellular release. During secretion, these specialized, morphologically distinct carriers, termed eosinophil sombrero vesicles, are actively formed and direct differential and rapid release of eosinophil proteins. This review highlights recent discoveries concerning the organization of the human eosinophil secretory pathway. These discoveries are defining a broader role for large vesiculotubular carriers in the intracellular trafficking and secretion of proteins, including selective receptor-mediated mobilization and transport of cytokines.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenberg HF, Phipps S, Foster PS. Eosinophil trafficking in allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen EA, Taranova AG, Lee NA, Lee JJ. Eosinophils: singularly destructive effector cells or purveyors of immunoregulation? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1313–1320. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:147–174. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ. Mechanisms of eosinophil-associated inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:651–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

