Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 17875987
- PMCID: PMC2000550
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707351104
Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells
Abstract
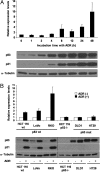
Accumulating evidence suggests a role for microRNAs in human carcinogenesis as novel types of tumor suppressors or oncogenes. However, their precise biological role remains largely elusive. In the present study, we aimed to identify microRNA species involved in the regulation of cell proliferation. Using quantitative RT-PCR analysis, we demonstrated that miR-34a was highly up-regulated in a human colon cancer cell line, HCT 116, treated with a DNA-damaging agent, adriamycin. Transient introduction of miR-34a into two human colon cancer cell lines, HCT 116 and RKO, caused complete suppression of cell proliferation and induced senescence-like phenotypes. Moreover, miR-34a also suppressed in vivo growth of HCT 116 and RKO cells in tumors in mice when complexed and administered with atelocollagen for drug delivery. Gene-expression microarray and immunoblot analyses revealed down-regulation of the E2F pathway by miR-34a introduction. Up-regulation of the p53 pathway was also observed. Furthermore, 9 of 25 human colon cancers (36%) showed decreased expression of miR-34a compared with counterpart normal tissues. Our results provide evidence that miR-34a functions as a potent suppressor of cell proliferation through modulation of the E2F signaling pathway. Abrogation of miR-34a function could contribute to aberrant cell proliferation, leading to colon cancer development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

