Biomarker method validation in anticancer drug development
- PMID: 17876307
- PMCID: PMC2259203
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707441
Biomarker method validation in anticancer drug development
Abstract
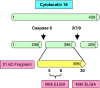
Over recent years the role of biomarkers in anticancer drug development has expanded across a spectrum of applications ranging from research tool during early discovery to surrogate endpoint in the clinic. However, in Europe when biomarker measurements are performed on samples collected from subjects entered into clinical trials of new investigational agents, laboratories conducting these analyses become subject to the Clinical Trials Regulations. While these regulations are not specific in their requirements of research laboratories, quality assurance and in particular assay validation are essential. This review, therefore, focuses on a discussion of current thinking in biomarker assay validation. Five categories define the majority of biomarker assays from 'absolute quantitation' to 'categorical'. Validation must therefore take account of both the position of the biomarker in the spectrum towards clinical end point and the level of quantitation inherent in the methodology. Biomarker assay validation should be performed ideally in stages on 'a fit for purpose' basis avoiding unnecessarily dogmatic adherence to rigid guidelines but with careful monitoring of progress at the end of each stage. These principles are illustrated with two specific examples: (a) absolute quantitation of protein biomarkers by mass spectrometry and (b) the M30 and M65 ELISA assays as surrogate end points of cell death.
Figures



References
-
- Aebersold R, Goodlett DR. Mass spectrometry in proteomics. Chem Rev. 2001;101:269–295. - PubMed
-
- Baggerly KA, Morris JS, Coombes KR. Reproducibility of SELDI-TOF protein patterns in serum: comparing datasets from different experiments. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:777–785. - PubMed
-
- Baggerly KA, Morris JS, Edmonson SR, Coombes KR. Signal in noise: evaluating reported reproducibility of serum proteomic tests for ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:307–309. - PubMed
-
- Bantel H, Lugering A, Heidemann J, Volkmann X, Poremba C, Strassburg CP, et al. Detection of apoptotic caspase activation in sera from patients with chronic HCV infection is associated with fibrotic liver injury. Hepatology. 2004;40:1078–1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

