Comprehensive characterization of serum clinical chemistry parameters and the identification of urinary superoxide dismutase in a carbon tetrachloride-induced model of hepatic fibrosis in the female Hanover Wistar rat
- PMID: 17877538
- PMCID: PMC2517331
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2007.00543.x
Comprehensive characterization of serum clinical chemistry parameters and the identification of urinary superoxide dismutase in a carbon tetrachloride-induced model of hepatic fibrosis in the female Hanover Wistar rat
Abstract
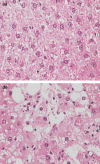
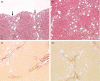
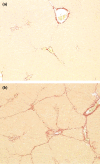
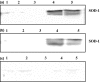
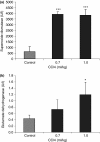
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)) was used to induce liver fibrosis in the rat. Using this model, we have identified changes in serum and urinary clinical chemistry parameters, and characterized histopathological lesions in the liver. Two experiments were conducted. In Experiment 1, rats were dosed at six levels of CCl(4) (0.06-0.36 ml/kg) twice weekly for 6 weeks, followed by a 6-week non-dosing recovery period (week 12). Livers were removed for histology at 6 and 12 weeks and serum parameters analysed. In Experiment 2, rats were given seven dose levels of CCl(4) (0.4-1.0 ml/kg) twice weekly for 6 weeks, followed by a 6-week recovery period (week 12); urine samples were analysed at 3, 6, 9 and 12 weeks using one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Liver fibrosis was evident at 6 weeks in Experiments 1 and 2, and the activity of serum enzymes (including alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and glutamate dehydrogenase) was increased. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis (Experiment 2) revealed a protein band at 18.4 kDa in urine from rats treated with CCl(4), not present in control urine, which was identified as copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn SOD). Western blotting revealed that SOD was increased in urine from rats treated with CCl(4) at 3 and 6 weeks, but not at 9 and 12 weeks. We conclude that Cu/Zn SOD is a urinary marker of hepatic necrosis, but not hepatic fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dose response and time course studies on superoxide dismutase as a urinary biomarker of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in the Hanover Wistar rat.Int J Exp Pathol. 2009 Oct;90(5):500-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00666.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19765104 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of superoxide dismutase as a potential urinary marker of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic toxicity.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Sep;46(9):2972-83. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.05.041. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18586068
-
Markers of experimental acute inflammation in the Wistar Han rat with particular reference to haptoglobin and C-reactive protein.Arch Toxicol. 2003 Jul;77(7):392-402. doi: 10.1007/s00204-003-0458-7. Epub 2003 Mar 22. Arch Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12669191
-
Identification of urinary microRNA profiles in rats that may diagnose hepatotoxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Feb;125(2):335-44. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr321. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22112502
-
Green tea extract supplementation ameliorates CCl4-induced hepatic oxidative stress, fibrosis, and acute-phase protein expression in rat.J Formos Med Assoc. 2012 Oct;111(10):550-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2011.06.026. Epub 2012 Mar 9. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012. PMID: 23089690
Cited by
-
Restorative effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on hepatic function in an experimental regression model of hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jan;15(1):47-56. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5965. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 27909717 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Mentha piperita L. leaf essential oil against CCl4 induced hepatic oxidative damage and renal failure in rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jan 9;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0645-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29316974 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin protects rat liver from CCl(4)-induced fibrogenesis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cells activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Oct 14;15(38):4753-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4753. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19824107 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Silymarin and Quercetin in a Miniaturized Scaffold in Wistar Rats against Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.ACS Omega. 2021 Aug 3;6(32):20735-20745. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00555. eCollection 2021 Aug 17. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34423182 Free PMC article.
-
Dose response and time course studies on superoxide dismutase as a urinary biomarker of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in the Hanover Wistar rat.Int J Exp Pathol. 2009 Oct;90(5):500-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00666.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19765104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham P, Wilfred G, Cathrine SP. Oxidative damage to the lipids and proteins of the lungs, testis and kidney of rats during carbon tetrachloride intoxication. Clim. Chim. Acta. 1999;289:177–179. - PubMed
-
- Abraham P, Wilfred G, Ramakrishna B. Plasma prolidase may be an index of liver fibrosis in the rat. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2000;295:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Al-Bader A, Mathew TC, Abul H, Al-Sayer H, Singal PK, Dashti HM. Cholangiocarcinoma and liver cirrhosis in relation to changes due to thioacetamide. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2000;208:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Arthur MJ. Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1525–1528. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee D, Madhusoodana UK, Nayak S, Jacob J. Urinary hydrogen peroxide: a probable marker of oxidative stress in malignancy. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2003;334:205–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

