PADB: published association database
- PMID: 17877839
- PMCID: PMC2039752
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-348
PADB: published association database
Abstract
Background: Although molecular pathway information and the International HapMap Project data can help biomedical researchers to investigate the aetiology of complex diseases more effectively, such information is missing or insufficient in current genetic association databases. In addition, only a few of the environmental risk factors are included as gene-environment interactions, and the risk measures of associations are not indexed in any association databases.
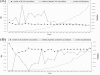
Description: We have developed a published association database (PADB; http://www.medclue.com/padb) that includes both the genetic associations and the environmental risk factors available in PubMed database. Each genetic risk factor is linked to a molecular pathway database and the HapMap database through human gene symbols identified in the abstracts. And the risk measures such as odds ratios or hazard ratios are extracted automatically from the abstracts when available. Thus, users can review the association data sorted by the risk measures, and genetic associations can be grouped by human genes or molecular pathways. The search results can also be saved to tab-delimited text files for further sorting or analysis. Currently, PADB indexes more than 1,500,000 PubMed abstracts that include 3442 human genes, 461 molecular pathways and about 190,000 risk measures ranging from 0.00001 to 4878.9.
Conclusion: PADB is a unique online database of published associations that will serve as a novel and powerful resource for reviewing and interpreting huge association data of complex human diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MedRefSNP: a database of medically investigated SNPs.Hum Mutat. 2009 Mar;30(3):E460-6. doi: 10.1002/humu.20914. Hum Mutat. 2009. PMID: 19105187
-
MutaGeneSys: estimating individual disease susceptibility based on genome-wide SNP array data.Bioinformatics. 2008 Feb 1;24(3):440-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm587. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18048395
-
Searching Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) for information for genetic loci involved in human disease.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2002 Aug;Chapter 1:Unit 1.2. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0102s00. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 18792932
-
[International HapMap project].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Dec;63 Suppl 12:29-34. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 16416767 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
[Development of genome-wide association database].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008 Jun;53(7):882-7. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008. PMID: 18536350 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Human Gene Mutation Database: 2008 update.Genome Med. 2009 Jan 22;1(1):13. doi: 10.1186/gm13. Genome Med. 2009. PMID: 19348700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hulbert EM, Smink LJ, Adlem EC, Allen JE, Burdick DB, Burren OS, Cavnor CC, Dolman GE, Flamez D, Friery KF, Healy BC, Killcoyne SA, Kutlu B, Schuilenburg H, Walker NM, Mychaleckyj J, Eizirik DL, Wicker LS, Todd JA, Goodman N. T1DBase: integration and presentation of complex data for type 1 diabetes research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D742–6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl933. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

