Establishment and primary application of a mouse model with hepatitis B virus replication
- PMID: 17879401
- PMCID: PMC4171321
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5324
Establishment and primary application of a mouse model with hepatitis B virus replication
Abstract
Aim: To establish a rapid and convenient animal model with hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication.
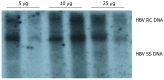
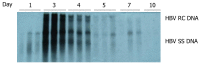
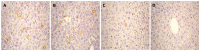
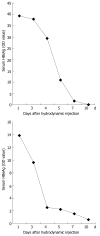
Methods: A naked DNA solution of HBV-replication-competent plasmid was transferred to BALB/C mice via the tail vein, using a hydrodynamic in vivo transfection procedure. After injection, these mice were sacrificed on d 1, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 10. HBV DNA replication intermediates in the liver were analyzed by Southern blot hybridization. The expression of hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) and hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the liver was checked by immunohistochemistry. Serum HBsAg and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Inhibition of HBV replication was compared in HBV replication model mice treated intraperitoneally with polyinosinic-polytidylin acid (polyIC) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
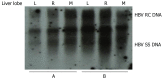
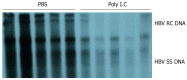
Results: After hydrodynamic in vivo transfection, HBV DNA replication intermediates in the mouse liver were detectable on d 1 and abundant on d 3 and 4, the levels were slightly decreased and remained relatively stable between d 5 and 7, and were almost undetectable on d 10. The expression patterns of HBcAg and HBsAg were similar to that of HBV replication intermediate DNA, except that they reached a peak on d 1 after injection. No obvious differences in HBV DNA replication intermediates were observed in the left, right and middle lobes of the liver. After treatment with polyIC, the level of HBV intermediate DNA in the liver was lower than that in the control mice injected with PBS.
Conclusion: A rapid and convenient mouse model with a high level of HBV replication was developed and used to investigate the inhibitory effect of polyIC on HBV replication, which provides a useful tool for future functional studies of the HBV genome.
Figures

References
-
- Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC, Chien CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981;2:1129–1133. - PubMed
-
- Liu FJ, Liu C, Deng LY, Zhou TY, Liu L, Tang H. Hydrodynamics-based in vivo transfection results in high level expression of HBsAg in mouse liver. Huaxi Yixue. 2005;20:697–699.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

