DNA methylation and histone acetylation work in concert to regulate memory formation and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 17881251
- PMCID: PMC2430891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2007.07.016
DNA methylation and histone acetylation work in concert to regulate memory formation and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
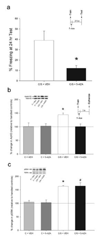
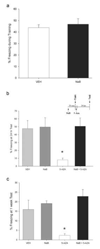
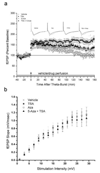
A clear understanding is developing concerning the importance of epigenetic-related molecular mechanisms in transcription-dependent long-term memory formation. Chromatin modification, in particular histone acetylation, is associated with transcriptional activation, and acetylation of histone 3 (H3) occurs in Area CA1 of the hippocampus following contextual fear conditioning training. Conversely, DNA methylation is associated with transcriptional repression, but is also dynamically regulated in Area CA1 following training. We recently reported that inhibition of the enzyme responsible for DNA methylation, DNA methyltransferase (DNMT), in the adult rat hippocampus blocks behavioral memory formation. Here, we report that DNMT inhibition also blocks the concomitant memory-associated H3 acetylation, without affecting phosphorylation of its upstream regulator, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). Interestingly, the DNMT inhibitor-induced deficit in memory consolidation, along with deficits in long-term potentiation, can be rescued by pharmacologically increasing levels of histone acetylation prior to DNMT inhibition. These observations suggest that DNMT activity is not only necessary for memory and plasticity, but that DNA methylation may work in concert with histone modifications to regulate plasticity and memory formation in the adult rat hippocampus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic alterations in the lateral amygdala are required for reconsolidation of a Pavlovian fear memory.Learn Mem. 2011 Aug 25;18(9):579-93. doi: 10.1101/lm.2243411. Print 2011 Sep. Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21868438 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic alterations are critical for fear memory consolidation and synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019958. Epub 2011 May 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625500 Free PMC article.
-
G9a/GLP histone lysine dimethyltransferase complex activity in the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex is required for gene activation and silencing during memory consolidation.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 18;32(16):5440-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0147-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22514307 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone acetylation: molecular mnemonics on the chromatin.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Feb;14(2):97-111. doi: 10.1038/nrn3427. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23324667 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic mechanisms involved in methamphetamine addiction.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 26;13:984997. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984997. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of epigenetics in stress-enhanced fear learning models of PTSD.Learn Mem. 2016 Sep 15;23(10):576-86. doi: 10.1101/lm.040485.115. Print 2016 Oct. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27634148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting specific HATs for neurodegenerative disease treatment: translating basic biology to therapeutic possibilities.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 28;7:30. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00030. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23543406 Free PMC article.
-
Aging-associated excess formaldehyde leads to spatial memory deficits.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1807. doi: 10.1038/srep01807. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23657727 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Memory and Cognitive Decline Associated with Aging and Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 13;22(22):12280. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212280. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Touzani K, Vronskaya S, Ishii S, Kandel ER, Barco A. Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP+/− mice: a model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron. 2004;42:947–959. - PubMed
-
- Becker PB, Ruppert S, Schutz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987;51:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Collins AL, Levenson JM, Vilaythong AP, Richman R, Armstrong DL, Noebels JL, Sweatt JD, Zoghbi HY. Mild overexpression of MeCP2 causes a progressive neurological disorder in mice. Human Molecular Genetics. 2004;13:2679–2689. - PubMed
-
- Cross SH, Meehan RR, Nan X, Bird A. A component of the transcriptional repressor MeCP1 shares a motif with DNA methyltransferase and HRX proteins. Nature Genetics. 1997;16:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Fischer A, Sananabenesi F, Wang X, Dobbin M, Tsai LH. Recovery of learning and memory is associated with chromatin remodelling. Nature. 2007;447:178–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

