Interkinetic nuclear migration and the selection of neurogenic cell divisions during vertebrate retinogenesis
- PMID: 17881520
- PMCID: PMC6672676
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2754-07.2007
Interkinetic nuclear migration and the selection of neurogenic cell divisions during vertebrate retinogenesis
Abstract
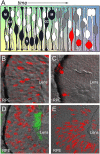
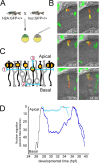
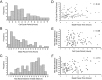
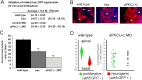
During retinal development, neuroepithelial progenitor cells divide in either a symmetric proliferative mode, in which both daughter cells remain mitotic, or in a neurogenic mode, in which at least one daughter cell exits the cell cycle and differentiates as a neuron. Although the cellular mechanisms of neurogenesis remain unknown, heterogeneity in cell behaviors has been postulated to influence this cell fate. In this study, we analyze interkinetic nuclear migration, the apical-basal movement of nuclei in phase with the cell cycle, and the relationship of this cell behavior to neurogenesis. Using time-lapse imaging in zebrafish, we show that various parameters of interkinetic nuclear migration are significantly heterogeneous among retinal neuroepithelial cells. We provide direct evidence that neurogenic progenitors have greater basal nuclei migrations during the last cell cycle preceding a terminal mitosis. In addition, we show that atypical protein kinase C (aPKC)-mediated cell polarity is essential for the relationship between nuclear position and neurogenesis. Loss of aPKC also resulted in increased proliferative cell divisions and reduced retinal neurogenesis. Our data support a novel model for neurogenesis, in which interkinetic nuclear migration differentially positions nuclei in neuroepithelial cells and therefore influences selection of progenitors for cell cycle exit based on apical-basal polarized signals.
Figures



References
-
- Alexiades MR, Cepko C. Quantitative analysis of proliferation and cell cycle length during development of the rat retina. Dev Dyn. 1996;205:293–307. - PubMed
-
- Biehlmaier O, Neuhauss SC, Kohler K. Onset and time course of apoptosis in the developing zebrafish retina. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;306:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Calegari F, Huttner WB. An inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases that lengthens, but does not arrest, neuroepithelial cell cycle induces premature neurogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:4947–4955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
