Wnt5a inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cells and enhances repopulation
- PMID: 17881570
- PMCID: PMC1986571
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704747104
Wnt5a inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cells and enhances repopulation
Abstract
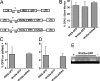
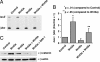
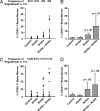
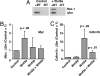
The mechanisms that regulate hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) fate decisions between proliferation and multilineage differentiation are unclear. Members of the Wnt family of ligands that activate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, which utilizes beta-catenin to relay the signal, have been demonstrated to regulate HSC function. In this study, we examined the role of noncanonical Wnt signaling in regulating HSC fate. We observed that noncanonical Wnt5a inhibited Wnt3a-mediated canonical Wnt signaling in HSCs and suppressed Wnt3a-mediated alterations in gene expression associated with HSC differentiation, such as increased expression of myc. Wnt5a increased short- and long-term HSC repopulation by maintaining HSCs in a quiescent G(0) state. From these data, we propose that Wnt5a regulates hematopoiesis by the antagonism of the canonical Wnt pathway, resulting in a pool of quiescent HSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Discrete roles of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoiesis and lymphopoiesis.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Nov 19;6(11):e1981. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.326. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26583322 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and repopulation through the Ryk receptor.Stem Cells. 2014 Jan;32(1):105-15. doi: 10.1002/stem.1513. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 23939973 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt-5A/B Signaling in Hematopoiesis throughout Life.Cells. 2020 Jul 29;9(8):1801. doi: 10.3390/cells9081801. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32751131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrasting responses of lymphoid progenitors to canonical and noncanonical Wnt signals.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 15;181(6):3955-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3955. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18768850 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hematopoiesis and the hematopoietic stem cell niche by Wnt signaling pathways.Cell Res. 2007 Sep;17(9):746-58. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.69. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17768401 Review.
Cited by
-
RhoA/Rock activation represents a new mechanism for inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the aging-associated bone loss.Cell Regen. 2021 Mar 3;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13619-020-00071-3. Cell Regen. 2021. PMID: 33655459 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt11 promotes cardiomyocyte development by caspase-mediated suppression of canonical Wnt signals.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;31(1):163-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01539-09. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21041481 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell regeneration through paracrine regulation of the Wnt5a/Prox1 signaling axis.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jun 15;132(12):e155914. doi: 10.1172/JCI155914. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35703178 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour Microenvironment Stress Promotes the Development of Drug Resistance.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;10(11):1801. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111801. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt5a expression in the hindgut of fetal rats with chemically induced anorectal malformations--studies in the ETU rat model.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011 Apr;26(4):493-9. doi: 10.1007/s00384-010-1125-0. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011. PMID: 21212964
References
-
- Kondo M, Wagers AJ, Manz MG, Prohaska SS, Scherer DC, Beilhack GF, Shizuru JA, Weissman IL. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:759–806. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, Clevers H. Nature. 2005;434:843–850. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, Duncan AW, Ailles L, Domen J, Scherer DC, Willert K, Hintz L, Nusse R, Weissman IL. Nature. 2003;423:409–414. - PubMed
-
- Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, Muijtjens M, Jones C, Zehnder JL, Gotlib J, Li K, Manz MG, Keating A, et al. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:657–667. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

