Noncoding transcription controls downstream promoters to regulate T-cell receptor alpha recombination
- PMID: 17882258
- PMCID: PMC2034674
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601866
Noncoding transcription controls downstream promoters to regulate T-cell receptor alpha recombination
Abstract
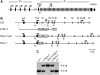
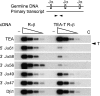
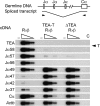
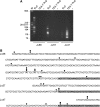
The T early alpha (TEA) promoter in the murine Tcra locus generates noncoding transcripts that extend across the 65 kb Jalpha array. Here, we have analyzed the significance of TEA transcription for Tcra locus regulation through the targeted introduction of a transcription terminator downstream of the TEA promoter. We demonstrate that noncoding transcription driven by this single promoter can instruct both positively and negatively the activity of downstream Jalpha promoters, and can similarly instruct alterations in Jalpha chromatin structure and Jalpha recombination. TEA transcription activates promoters associated with relatively proximal Jalpha segments and stimulates histone acetylation, histone methylation and chromatin accessibility in this region. In contrast, at more distal locations, TEA transcription inhibits promoter activity through transcriptional interference and suppresses chromatin accessibility. In combination, these effects target initial Valpha-to-Jalpha recombination to TEA-proximal Jalpha segments and promote the ordered usage of the Jalpha array. The ability of TEA transcription to coordinate the activity of multiple downstream promoters maximizes the biological potential of the Jalpha array and diversifies the Tcra repertoire.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TEA regulates local TCR-Jalpha accessibility through histone acetylation.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Aug;33(8):2216-22. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323867. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12884296
-
Tcrd Rearrangement Redirects a Processive Tcra Recombination Program to Expand the Tcra Repertoire.Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 6;19(10):2157-2173. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.045. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28591585 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor α enhancer is inactivated in αβ T lymphocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 7;112(14):E1744-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406551112. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25831496 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into the transcriptional control of the Tcra/Tcrd locus by distant enhancers during the development of T-lymphocytes.Transcription. 2015;6(4):65-73. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2015.1078429. Transcription. 2015. PMID: 26230488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin Dynamics and the Development of the TCRα and TCRδ Repertoires.Adv Immunol. 2015;128:307-61. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Adv Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26477370 Review.
Cited by
-
A Lamina-Associated Domain Border Governs Nuclear Lamina Interactions, Transcription, and Recombination of the Tcrb Locus.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 13;25(7):1729-1740.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.052. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30428344 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-7 receptor signaling is crucial for enhancer-dependent TCRδ germline transcription mediated through STAT5 recruitment.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 19;13:943510. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.943510. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059467 Free PMC article.
-
Control of V(D)J Recombination through Transcriptional Elongation and Changes in Locus Chromatin Structure and Nuclear Organization.Genet Res Int. 2011;2011:970968. doi: 10.4061/2011/970968. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Genet Res Int. 2011. PMID: 22567371 Free PMC article.
-
A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers.PLoS Biol. 2010 May 11;8(5):e1000384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000384. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20485488 Free PMC article.
-
RNA in unexpected places: long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;14(11):699-712. doi: 10.1038/nrm3679. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24105322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abarrategui I, Krangel MS (2006) Regulation of T cell receptor-α gene recombination by transcription. Nat Immunol 7: 1109–1115 - PubMed
-
- Baguet A, Sun X, Arroll T, Krumm A, Bix M (2005) Intergenic transcription is not required in Th2 cells to maintain histone acetylation and transcriptional permissiveness at the Il4-Il13 locus. J Immunol 175: 8146–8153 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Schneider R, Myers FA, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C, Kouzarides T (2005) Spatial distribution of di- and tri-methyl lysine 36 of histone H3 at active genes. J Biol Chem 280: 17732–17736 - PubMed
-
- Belotserkovskaya R, Oh S, Bondarenko VA, Orphanides G, Studitsky VM, Reinberg D (2003) FACT facilitates transcription-dependent nucleosome alteration. Science 301: 1090–1093 - PubMed
-
- Bolland DJ, Wood AL, Johnston CM, Bunting SF, Morgan G, Chakalova L, Fraser PJ, Corcoran AE (2004) Antisense intergenic transcription in V(D)J recombination. Nat Immunol 5: 630–637 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

