Alpha2-adrenoceptors couple to inhibition of R-type calcium currents in myenteric neurons
- PMID: 17883436
- PMCID: PMC2680314
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00976.x
Alpha2-adrenoceptors couple to inhibition of R-type calcium currents in myenteric neurons
Abstract
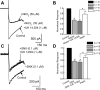
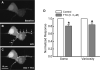
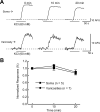
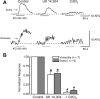
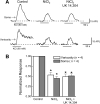
Alpha2-adrenoceptors inhibit Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels throughout the nervous system and Ca2+ channel function is modulated following activation of some G-protein coupled receptors. We studied the specific Ca2+ channel inhibited following alpha2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig small intestinal myenteric neurons. Ca2+ currents (I(Ca2+)) were studied using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques. Changes in intracellular Ca2+ (delta[Ca2+]i) in nerve cell bodies and varicosities were studied using digital imaging where Ca2+ influx was evoked by KCl (60 mmol L(-1)) depolarization. The alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, UK 14 304 (0.01-1 micromol L(-1)) inhibited I(Ca2+) and delta[Ca2+]i; maximum inhibition of I(Ca2+) was 40%. UK 14 304 did not affect I(Ca2+) in the presence of SNX-482 or NiCl2 (R-type Ca2+ channel antagonists). UK 14 304 inhibited I(Ca2+) in the presence of nifedipine, omega-agatoxin IVA or omega-conotoxin, inhibitors of L-, P/Q- and N-type Ca2+ channels. UK 14 304 induced inhibition of I(Ca2+) was blocked by pertussis toxin pretreatment (1 microg mL(-1) for 2 h). Alpha2-adrenoceptors couple to inhibition of R-type Ca2+ channels via a pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway in myenteric neurons. R-type channels may be a target for the inhibitory actions of noradrenaline released from sympathetic nerves on to myenteric neurons.
Figures
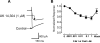
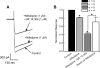
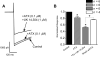
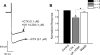
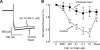

Similar articles
-
R-type calcium channels in myenteric neurons of guinea pig small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Jul;287(1):G134-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00532.2003. Epub 2004 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14988068
-
Activation of alpha 2-adrenoceptors causes inhibition of calcium channels but does not modulate inwardly-rectifying K+ channels in caudal raphe neurons.Neuroscience. 1998 Feb;82(3):753-65. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00312-6. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9483533
-
3,4-Diaminopyridine masks the inhibition of noradrenaline release from chick sympathetic neurons via presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors: insights into the role of N- and L-type calcium channels.Brain Res. 1996 May 20;721(1-2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00169-2. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8793089
-
Inhibition of N-type calcium channels: the only mechanism by which presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors control sympathetic transmitter release.Eur J Neurosci. 1996 Sep;8(9):1924-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01336.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8921283
-
A somatostatin receptor inhibits noradrenaline release from chick sympathetic neurons through pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanisms: comparison with the action of alpha 2-adrenoceptors.Neuroscience. 1996 Jul;73(2):595-604. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00074-7. Neuroscience. 1996. PMID: 8783273
Cited by
-
Composition and Antidiarrheal Activity of Bidens odorata Cav.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:170290. doi: 10.1155/2013/170290. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24282432 Free PMC article.
-
R-Type Ca2+ channels couple to inhibitory neurotransmission to the longitudinal muscle in the guinea-pig ileum.Exp Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;102(3):299-313. doi: 10.1113/EP086027. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28008669 Free PMC article.
-
Individual sympathetic postganglionic neurons coinnervate myenteric ganglia and smooth muscle layers in the gastrointestinal tract of the rat.J Comp Neurol. 2016 Sep 1;524(13):2577-603. doi: 10.1002/cne.23978. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26850701 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic analysis of neuromuscular transmission in the colon of ChAT-ChR2-YFP BAC transgenic mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):G569-G579. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00089.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31411893 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of TRPV2 activation in intestinal movement through nitric oxide production in mice.J Neurosci. 2010 Dec 8;30(49):16536-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4426-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21147993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furness JB. The enteric nervous system. 1st edition Blackwell Publishing, Incorporated; 2006.
-
- Kunze WA, Furness JB. The enteric nervous system and regulation of intestinal motility. Ann Rev Physiol. 1999;61:117–42. - PubMed
-
- Furness JB, Jones C, Nurgali K, Clerc N. Intrinsic primary afferent neurons and nerve circuits within the intestine. Prog Neurobiol. 2004;72:143–64. - PubMed
-
- Vogalis F, Furness JB, Kunze WA. Afterhyperpolarization current in myenteric neurons of the guinea pig duodenum. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:1941–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

