Moderate level fetal alcohol exposure and serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism affect neonatal temperament and limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation in monkeys
- PMID: 17884019
- PMCID: PMC2696278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.07.017
Moderate level fetal alcohol exposure and serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism affect neonatal temperament and limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation in monkeys
Abstract
Background: A length polymorphism in the serotonin (5-HT) transporter gene promoter region in humans and rhesus monkeys affects functional characteristics of the brain 5-HT system. Prenatal alcohol exposure (FA-exposure) can have an impact on brain and psychosocial development that could interact with genetic endowment. This study determined whether moderate FA-exposure interacts with polymorphism in the 5-HT transporter gene to increase the incidence or severity of fetal alcohol effects in rhesus monkeys.
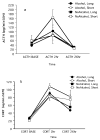
Methods: The offspring of monkeys who did or did not consume moderate amounts of alcohol during pregnancy were assessed for temperament as neonates and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol (CORT) in response to mother-infant separation at 6 months of age. Serotonin promoter region genotypes (homozygous s/s or heterozygous s/l versus homozygous l/l) were determined.
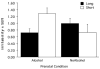
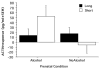
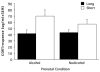
Results: Prenatal alcohol exposed carriers of the s allele exhibited increased neonatal irritability and increased ACTH and CORT compared with FA-exposed monkeys homozygous for the l allele and monkeys that were not FA-exposed regardless of genotype.
Conclusions: The s allele of the 5-HT transporter increases the probability of neonatal irritability and increased stress responsiveness in FA-exposed monkeys, and this gene-environment interaction may affect psychosocial development. It is probable that FA-exposure contributes to 5-HT transporter gene-environment interactions in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Moderate prenatal alcohol exposure and serotonin genotype interact to alter CNS serotonin function in rhesus monkey offspring.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 May;35(5):912-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01421.x. Epub 2011 Feb 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21294753 Free PMC article.
-
Rearing condition and rh5-HTTLPR interact to influence limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response to stress in infant macaques.Biol Psychiatry. 2004 Apr 1;55(7):733-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.12.008. Biol Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15039002
-
Moderate level alcohol during pregnancy, prenatal stress, or both and limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis response to stress in rhesus monkeys.Child Dev. 2004 Jan-Feb;75(1):96-109. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00656.x. Child Dev. 2004. PMID: 15015677
-
Serotonin transporter gene variation, infant abuse, and responsiveness to stress in rhesus macaque mothers and infants.Horm Behav. 2009 Apr;55(4):538-47. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Horm Behav. 2009. PMID: 19470363 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in the serotonin reuptake transporter gene modify the consequences of social status on metabolic health in female rhesus monkeys.Physiol Behav. 2008 Mar 18;93(4-5):807-19. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.11.042. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 18190935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on behavior: rodent and primate studies.Neuropsychol Rev. 2011 Jun;21(2):186-203. doi: 10.1007/s11065-011-9168-8. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Neuropsychol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21499982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and their transmission through genetic and epigenetic mechanisms.Front Genet. 2014 Jun 2;5:154. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00154. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24917878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The serotonin transporter gene is a substrate for age and stress dependent epigenetic regulation in rhesus macaque brain: potential roles in genetic selection and gene × environment interactions.Dev Psychopathol. 2012 Nov;24(4):1391-400. doi: 10.1017/S0954579412000788. Dev Psychopathol. 2012. PMID: 23062305 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of moderate level prenatal alcohol exposure influences gene expression of sensory processing behavior in rhesus monkeys.Front Integr Neurosci. 2009 Nov 10;3:30. doi: 10.3389/neuro.07.030.2009. eCollection 2009. Front Integr Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19936317 Free PMC article.
-
Who is at risk? Population characterization of alcohol self-administration in nonhuman primates helps identify pathways to dependence.Alcohol Res Health. 2008;31(4):289-97. Alcohol Res Health. 2008. PMID: 23584006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamer DH, Greenberg BD, Sabol SZ, Murphy DL. Role of the serotonin transporter gene in temperament and character. J Personal Disord. 1999;13:312–27. - PubMed
-
- Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A. Association of anxiety related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science. 1996;274:1527–1531. - PubMed
-
- Murphy DL, Lerner A, Rudnick G, Lesch KP. Serotonin transporter: gene, genetic disorders, and pharmacogenetics. Mol Interv. 2004;4:109–123. - PubMed
-
- Reif A, Lesch KP. Toward a molecular architecture of personality. Behav Brain Res. 2003;139:1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

