Noradrenergic modulation of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area
- PMID: 17884297
- PMCID: PMC2254936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.08.009
Noradrenergic modulation of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area
Abstract
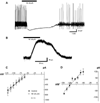
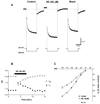
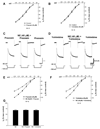
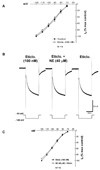
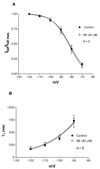
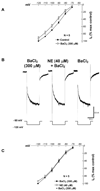
Alterations in the state of excitability of midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) may underlie changes in the synaptic plasticity of the mesocorticolimbic system. Here, we investigated norepinephrine's (NE) regulation of VTA DA cell excitability by modulation of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current, Ih, with whole cell recordings in rat brain slices. Current clamp recordings show that NE (40 microM) hyperpolarizes spontaneously firing VTA DA cells (11.23+/-4 mV; n=8). In a voltage clamp, NE (40 microM) induces an outward current (100+/-24 pA; n=8) at -60 mV that reverses at about the Nernst potential for potassium (-106 mV). In addition, NE (40 microM) increases the membrane cord conductance (179+/-42%; n=10) and reduces Ih amplitude (68+/-3% of control at -120 mV; n=10). The noradrenergic alpha-1 antagonist prazosin (40 microM; n=5) or the alpha-2 antagonist yohimbine (40 microM; n=5) did not block NE effects. All NE-evoked events were blocked by the D2 antagonists sulpiride (1 microM) and eticlopride (100 nM) and no significant reduction of Ih took place in the presence of the potassium channel blocker BaCl2 (300 microM). Therefore, it is concluded that NE inhibition of Ih was due to an increase in membrane conductance by a nonspecific activation of D2 receptors that induce an outward potassium current and is not a result of a second messenger system acting on h-channels. The results also suggest that Ih channels are mainly located at dendrites of VTA DA cells and, thus, their inhibition may facilitate the transition from single-spike firing to burst firing and vice versa.
Figures
References
-
- Battaglia G, et al. Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor knockout mice are protected against methamphetamine toxicity. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2003;86:413–421. - PubMed
-
- Berger T, et al. Hyperpolarization-activated current Ih disconnects somatic and dendritic spike initiation zones in layer V pyramidal neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2003;90:2428–2437. - PubMed
-
- Berger T, et al. High Ih channel density in the distal apical dendrite of layer V pyramidal cells increases bidirectional attenuation of EPSPs. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2001;85:855–868. - PubMed
-
- Cathala L, et al. Alpha-2 adrenoreceptor activation increases a cationic conductance and spontaneous gabaergic synaptic activity in dopaminergic neurones of the rat substantia nigra. Neuroscience. 2002;115(4):1059–1065. - PubMed
-
- Cathala L, Paupardin-Tritsch D. Effect of catecholamines on the hyperpolarization-activated Ih and the inward rectifying potassium Ikir currents in the rat’s substantia nigra pars compacta. European J. of Neuroscience. 1999;11:398–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

