Developmental changes in activation and effective connectivity in phonological processing
- PMID: 17884585
- PMCID: PMC2638503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.048
Developmental changes in activation and effective connectivity in phonological processing
Abstract
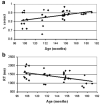
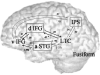
The current study examined developmental changes in activation and effective connectivity among brain regions during a phonological processing task, using fMRI. Participants, ages 9-15, were scanned while performing rhyming judgments on pairs of visually presented words. The orthographic and phonological similarity between words in the pair was independently manipulated, so that rhyming judgment could not be based on orthographic similarity. Our results show a developmental increase in activation in the dorsal part of left inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), accompanied by a decrease in the dorsal part of left superior temporal gyrus (STG). The coupling of dorsal IFG with other selected brain regions involved in the phonological decision increased with age, while the coupling of STG decreased with age. These results suggest that during development there is a shift from reliance on sensory auditory representations to reliance on phonological segmentation and covert articulation for performing rhyming judgment on visually presented words. In addition, we found a developmental increase in activation in left posterior parietal cortex that was not accompanied by a change in its connectivity with the other regions. These results suggest that maturational changes within a cortical region are not necessarily accompanied by an increase in its interactions with other regions and its contribution to the task. Our results are consistent with the idea that there is reduced reliance on primary sensory processes as task-relevant processes mature and become more efficient during development.
Figures



References
-
- Baayen RH, Piepenbrock R, Gulikers L. The CELEX Lexical Database (Version Release 2) [CD-ROM] Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania; Philadelphia, PA: 1995.
-
- Belin P, Zatorre RJ, Ahad P. Human temporal-lobe response to vocal sounds. Cogn. Brain Res. 2002;13:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Binder JR, Frost JA, Hammeke TA, Bellgowan PSF, Springer JA, Kaufman JN, Possing ET. Human temporal lobe activation by speech and nonspeech sounds. Cereb. Cortex. 2000;10:512–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

