SAGETTARIUS: a program to reduce the number of tags mapped to multiple transcripts and to plan SAGE sequencing stages
- PMID: 17884916
- PMCID: PMC2094080
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm648
SAGETTARIUS: a program to reduce the number of tags mapped to multiple transcripts and to plan SAGE sequencing stages
Abstract
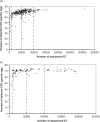
SAGE (Serial Analysis of Gene Expression) experiments generate short nucleotide sequences called 'tags' which are assumed to map unambiguously to their original transcripts (1 tag to 1 transcript mapping). Nevertheless, many tags are generated that do not map to any transcript or map to multiple transcripts. Current bioinformatics resources, such as SAGEmap and TAGmapper, have focused on reducing the number of unmapped tags. Here, we describe SAGETTARIUS, a new high-throughput program that performs successive precise Nla3 and Sau3A tag to transcript mapping, based on specifically designed Virtual Tag (VT) libraries. First, SAGETTARIUS decreases the number of tags mapped to multiple transcripts. Among the various mapping resources compared, SAGETTARIUS performed the best in this respect by decreasing up to 11% the number of multiply mapped tags. Second, SAGETTARIUS allows the establishment of a guideline for SAGE experiment sequencing efforts through efficient mapping of the CRT (Cytoplasmic Ribosomal protein Transcripts)-specific tags. Using all publicly available human and mouse Nla3 SAGE experiments, we show that sequencing 100,000 tags is sufficient to map almost all CRT-specific tags and that four sequencing stages can be identified when carrying out a human or mouse SAGE project. SAGETTARIUS is web interfaced and freely accessible to academic users.
Figures

References
-
- Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick M, Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR, Wu A, Olde B, et al. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991;252:1651–1656. - PubMed
-
- Liang P, Pardee AB. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992;257:967–971. - PubMed
-
- Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, Zhu XZ, Rinn JL, Tongprasit W, Samanta M, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling array. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
-
- Velculescu VE, Zhang L, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science. 1995;270:484–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

