Multitensor tractography enables better depiction of motor pathways: initial clinical experience using diffusion-weighted MR imaging with standard b-value
- PMID: 17885245
- PMCID: PMC8134192
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A0640
Multitensor tractography enables better depiction of motor pathways: initial clinical experience using diffusion-weighted MR imaging with standard b-value
Abstract
Background and purpose: The purpose of this work was to test the feasibility of using high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI)-based multitensor tractography to depict motor pathways in patients with brain tumors.
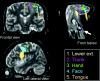
Materials and methods: Ten patients (6 males and 4 females) with a mean age of 52 years (range, 9-77 years) were scanned using a 1.5T clinical MR unit. Single-shot echo-planar imaging was used for diffusion-weighted imaging (repetition time, 6000 ms; excitation time, 88 ms) with a diffusion-sensitizing gradient in 32 orientations and a b-value of 1000 s/mm(2). Data postprocessing was performed using both the conventional single- and multitensor methods. The depiction rate of the 5 major components of the motor pathways, that is, the lower extremity, trunk, hand, face, and tongue, was assessed.
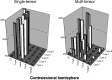
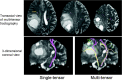
Results: Motor fibers on both lesional and contralesional sides were successfully depicted by both the single-tensor and multitensor techniques. However, with the single-tensor model, the depiction of motor pathways was typically limited to the fibers of trunk areas. With the multitensor technique, at least 4 of 5 major fiber bundles arising from the primary motor cortex could be identified.
Conclusion: HARDI-based multitensor tractography using a standard b-value (1000 s/mm(2)) can depict the fiber tracts from the face and tongue regions of the primary motor cortex.
Figures


References
-
- Iwasaki S, Nakagawa H, Fukusumi A, et al. Identification of pre- and postcentral gyri on CT and MR images on the basis of the medullary pattern of cerebral white matter. Radiology 1991;179:207–13 - PubMed
-
- Naidich TP, Valavanis AG, Kubik S. Anatomic relationships along the low-middle convexity: Part I–normal specimens and magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 1995;36:517–32 - PubMed
-
- Yousry TA, Schmid UD, Alkadhi H, et al. Localization of the motor hand area to a knob on the precentral gyrus. A new landmark. Brain 1997;120:141–57 - PubMed
-
- Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, et al. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1999;45:265–69 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
