Continuous glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 17889075
- PMCID: PMC2045068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.03.047
Continuous glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To examine the feasibility of daily use of a continuous glucose monitor, the FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System ("Navigator"), in children with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Study design: After a masked Navigator was used for 4 to 7 days to establish a baseline level of glycemic control, 30 insulin pump users with T1D (average age 11.2 years) were asked to use the Navigator daily for 13 weeks.
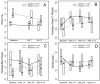
Results: Subjects averaged 149 h/wk of Navigator use during the first 4 weeks, which decreased slightly to 134 h/wk during weeks 9 to 13 (P = .006). Mean hemoglobin A1c improved from 7.1% at baseline to 6.8% at 13 weeks (P = .02), and the percentage of glucose values between 71 and 180 mg/dL increased from 52% to 60% (P = .01). Subjects and parents reported high satisfaction with the Navigator on the Continuous Glucose Monitor Satisfaction Scale. Two subjects had severe skin reactions related to sensor mount adhesive.
Conclusion: This study indicates that incorporating real-time continuous glucose monitoring into the daily treatment of children with T1D is feasible. The results provide a compelling rationale for conducting a randomized trial of daily use of a continuous glucose monitor in children with T1D.
Similar articles
-
Prolonged use of continuous glucose monitors in children with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or intensive multiple-daily injection therapy.Pediatr Diabetes. 2009 Apr;10(2):91-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00476.x. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19175899
-
Feasibility of prolonged continuous glucose monitoring in toddlers with type 1 diabetes.Pediatr Diabetes. 2012 Jun;13(4):301-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00837.x. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22151826 Free PMC article.
-
Closed-loop artificial pancreas using subcutaneous glucose sensing and insulin delivery and a model predictive control algorithm: preliminary studies in Padova and Montpellier.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009 Sep 1;3(5):1014-21. doi: 10.1177/193229680900300504. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009. PMID: 20144414 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes technology and treatments in the paediatric age group.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011 Feb;(170):76-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02582.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21323816 Review.
-
An overview of continuous glucose monitoring and the ambulatory glucose profile.Minn Med. 2011 Aug;94(8):40-4. Minn Med. 2011. PMID: 21957816 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a self-administered oral glucose tolerance test.Diabetes Care. 2013 Jun;36(6):1483-8. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0643. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23321216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Validation of measures of satisfaction with and impact of continuous and conventional glucose monitoring.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010 Sep;12(9):679-84. doi: 10.1089/dia.2010.0015. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20799388 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring With Geriatric Principles in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes and Hypoglycemia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Diabetes Care. 2025 May 1;48(5):694-702. doi: 10.2337/dc24-1069. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 39325586 Clinical Trial.
-
The benefits, limitations, and cost-effectiveness of advanced technologies in the management of patients with diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015 Mar;9(2):320-30. doi: 10.1177/1932296814565661. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25555391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technological Ecological Momentary Assessment Tools to Study Type 1 Diabetes in Youth: Viewpoint of Methodologies.JMIR Diabetes. 2021 Jun 3;6(2):e27027. doi: 10.2196/27027. JMIR Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34081017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group A randomized multicenter trial comparing the GlucoWatch Biographer with standard glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1101–6. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group The accuracy of the Freestyle Navigator™ Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006 In press. - PubMed
-
- Draize JH, Woodward G, Calvary HO. Methods for the study of irritation and toxicity of substances applied topically to the skin and mucous membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1944;82:377–90.
-
- Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group Comparison of fingerstick hemoglobin A1c levels assayed by DCA 2000 with the DCCT/EDIC central laboratory assay: results of a Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2005;6:13–6. - PubMed
-
- Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Jacobs JR, Gottschalk M, Kaufman F, Jones KL. The PedsQL™ in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes: reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ Generic Core Scales and Type 1 Diabetes Module. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:631–7. - PubMed