Claw and limb disorders in 12 Norwegian beef-cow herds
- PMID: 17892582
- PMCID: PMC2034568
- DOI: 10.1186/1751-0147-49-24
Claw and limb disorders in 12 Norwegian beef-cow herds
Abstract
Background: The main aim of the study was to assess the prevalence of claw and limb disorders in Norwegian beef-cow herds.
Methods: Twenty-six herds with >or=15 cow-years were selected by computerized systematic assignment from the three most beef cattle-dense regions of Norway. The study population consisted of 12 herds with 28 heifers and 334 cows. The animals were trimmed and examined once by claw trimmers during the late winter and spring of 2003. The seven claw trimmers had been taught diagnosing and recording of claw lesions. Environment, feeding and management routines, age and breed, culling and carcass characteristics were also recorded.
Results: Lameness was recorded in 1.1% of the animals, and only in hind claws. Pericarpal swellings were recorded in one animal and peritarsal lesions in none. In total, claw and limb disorders including lameness were recorded in 29.6% of the animals, 4.1% with front and 28.2% with hind limb disorders, respectively. Most lesions were mild. Laminitis-related claw lesions were recorded in 18.0% of the animals and infectious lesions in 16.6%. The average claw length was 84 mm in front claws and 89 mm in hind claw. Both laminitis-related and infectious claw lesions were more prevalent with increasing age. Carcasses from animals with claw and limb disorders were on average 34 kg heavier than carcasses from animals without such disorders (p = 0.02). Our results also indicate association between some management factors and claw lesions.
Conclusion: The study shows that the prevalence of lameness was low in 12 Norwegian beef-cow herds compared to beef-cattle herds in other countries and also that there were less claw and limb disorders in these herds compared to foreign dairy-cattle herds. The prevalence of lameness and white-line fissures was approximately the same as in Norwegian dairy herds whereas less dermatitis, heel-horn erosions, haemorrhages of the sole and the white line and sole ulcers were recorded.
Figures
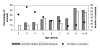


References
-
- Enting H, Kooij D, Dijkhuizen AA, Huirne RBM, Noordhuizen-Stassen EN. Economic losses due to clinical lameness in dairy cattle. Livest Prod Sci. 1997;49:259–267. doi: 10.1016/S0301-6226(97)00051-1. - DOI
-
- Roeber DL, Mies PD, Smith CD, Belk KE, Field TG, Tatum JD, Scanga JA, Smith GC. National market cow and bull beef quality audit-1999: a survey of producer-related defects in market cows and bulls. J Anim Sci. 2001;79:658–665. - PubMed
-
- Logue DN, Offer J, Kempson SA. Lameness in dairy cattle. Ir Vet J. 1993;46:47–58.
-
- Murray RD, Downham DY, Clarkson MJ, Faull WB, Hughes JW, Manson FJ, Meritt JB, Russel WB, Sutherst JE, Ward WR. Epidemiology of lameness in dairy cattle: description and analysis of foot lesions. Vet Rec. 1996;138:586–591. - PubMed
-
- Griffin D, Perino L, Hudson D. Feedlot lameness. University of Nebraska Extension Publication G93-1159-A. 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

