Endotoxemia and sepsis mortality reduction by non-anticoagulant activated protein C
- PMID: 17893198
- PMCID: PMC2118455
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070404
Endotoxemia and sepsis mortality reduction by non-anticoagulant activated protein C
Abstract
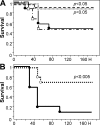
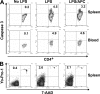
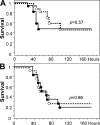
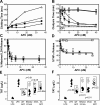
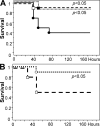
Activated protein C (APC) reduces mortality of severe sepsis patients but increases the risk of serious bleeding. APC exerts anticoagulant activity by proteolysis of factors Va/VIIIa. APC also exerts antiinflammatory and antiapoptotic effects and stabilizes endothelial barrier function by APC-initiated cell signaling that requires two receptors, endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) and protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1). The relative importance of APC's various activities for efficacy in sepsis is unknown. We used protein engineering of mouse APC and genetically altered mice to clarify mechanisms for the efficacy of APC in mouse sepsis models. Mortality reduction in LPS-induced endotoxemia required the enzymatic active site of APC, EPCR, and PAR-1, highlighting a key role for APC's cytoprotective actions. A recombinant APC variant with normal signaling but <10% anticoagulant activity (5A-APC) was as effective as wild-type APC in reducing mortality after LPS challenge, and enhanced the survival of mice subjected to peritonitis induced by gram-positive or -negative bacteria or to polymicrobial peritoneal sepsis triggered by colon ascendens stent implantation. Thus, APC's efficacy in severe sepsis is predominantly based on EPCR- and PAR1-dependent cell signaling, and APC variants with normal cell signaling but reduced anticoagulant activities retain efficacy while reducing the risk of bleeding.
Figures


References
-
- Esmon, C.T. 2006. Inflammation and the activated protein C anticoagulant pathway. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 32(Suppl. 1):49–60. - PubMed
-
- Mosnier, L.O., B.V. Zlokovic, and J.H. Griffin. 2007. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood. 109:3161–3172. - PubMed
-
- Dahlback, B., and B.O. Villoutreix. 2005. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C anticoagulant pathway: novel insights into structure-function relationships and molecular recognition. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25:1311–1320. - PubMed
-
- Joyce, D.E., L. Gelbert, A. Ciaccia, B. DeHoff, and B.W. Grinnell. 2001. Gene expression profile of antithrombotic protein c defines new mechanisms modulating inflammation and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276:11199–11203. - PubMed
-
- Riewald, M., R.J. Petrovan, A. Donner, B.M. Mueller, and W. Ruf. 2002. Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science. 296:1880–1882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

