Selective predisposition to bacterial infections in IRAK-4-deficient children: IRAK-4-dependent TLRs are otherwise redundant in protective immunity
- PMID: 17893200
- PMCID: PMC2118442
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070628
Selective predisposition to bacterial infections in IRAK-4-deficient children: IRAK-4-dependent TLRs are otherwise redundant in protective immunity
Abstract
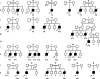
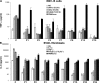
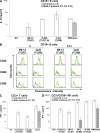
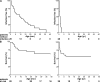
Human interleukin (IL) 1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4) deficiency is a recently discovered primary immunodeficiency that impairs Toll/IL-1R immunity, except for the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3- and TLR4-interferon (IFN)-alpha/beta pathways. The clinical and immunological phenotype remains largely unknown. We diagnosed up to 28 patients with IRAK-4 deficiency, tested blood TLR responses for individual leukocyte subsets, and TLR responses for multiple cytokines. The patients' peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) did not induce the 11 non-IFN cytokines tested upon activation with TLR agonists other than the nonspecific TLR3 agonist poly(I:C). The patients' individual cell subsets from both myeloid (granulocytes, monocytes, monocyte-derived dendritic cells [MDDCs], myeloid DCs [MDCs], and plasmacytoid DCs) and lymphoid (B, T, and NK cells) lineages did not respond to the TLR agonists that stimulated control cells, with the exception of residual responses to poly(I:C) and lipopolysaccharide in MDCs and MDDCs. Most patients (22 out of 28; 79%) suffered from invasive pneumococcal disease, which was often recurrent (13 out of 22; 59%). Other infections were rare, with the exception of severe staphylococcal disease (9 out of 28; 32%). Almost half of the patients died (12 out of 28; 43%). No death and no invasive infection occurred in patients older than 8 and 14 yr, respectively. The IRAK-4-dependent TLRs and IL-1Rs are therefore vital for childhood immunity to pyogenic bacteria, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae. Conversely, IRAK-4-dependent human TLRs appear to play a redundant role in protective immunity to most infections, at most limited to childhood immunity to some pyogenic bacteria.
Figures



References
-
- Picard, C., A. Puel, M. Bonnet, C.L. Ku, J. Bustamante, K. Yang, C. Soudais, S. Dupuis, J. Feinberg, C. Fieschi, et al. 2003. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK-4 deficiency. Science. 299:2076–2079. - PubMed
-
- Kuhns, D.B., D.A. Long Priel, and J.I. Gallin. 1997. Endotoxin and IL-1 hyporesponsiveness in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J. Immunol. 158:3959–3964. - PubMed
-
- Medvedev, A.E., A. Lentschat, D.B. Kuhns, J.C. Blanco, C. Salkowski, S. Zhang, M. Arditi, J.I. Gallin, and S.N. Vogel. 2003. Distinct mutations in IRAK-4 confer hyporesponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 1 in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J. Exp. Med. 198:521–531. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Currie, A.J., D.J. Davidson, G.S. Reid, S. Bharya, K.L. MacDonald, R.S. Devon, and D.P. Speert. 2004. Primary immunodeficiency to pneumococcal infection due to a defect in Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Pediatr. 144:512–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

