ZBP2 facilitates binding of ZBP1 to beta-actin mRNA during transcription
- PMID: 17893325
- PMCID: PMC2169170
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00972-07
ZBP2 facilitates binding of ZBP1 to beta-actin mRNA during transcription
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(9):2481
Abstract
Cytoplasmic mRNA localization regulates gene expression by spatially restricting protein translation. Recent evidence has shown that nuclear proteins (such as hnRNPs) are required to form mRNPs capable of cytoplasmic localization. ZBP1 and ZBP2, two hnRNP K homology domain-containing proteins, were previously identified by their binding to the zipcode, the sequence element necessary and sufficient for beta-actin mRNA localization. ZBP1 colocalizes with nascent beta-actin mRNA in the nucleus but is predominantly a cytoplasmic protein. ZBP2, in contrast, is predominantly nuclear. We hypothesized that the two proteins cooperate to localize beta-actin mRNA and sought to address where and how this might occur. We demonstrate that ZBP2, a homologue of the splicing factor KSRP, binds initially to nascent beta-actin transcripts and facilitates the subsequent binding of the shuttling ZBP1. ZBP1 then associates with the RNA throughout the nuclear export and cytoplasmic localization process.
Figures






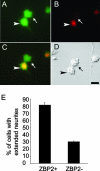
References
-
- Adams, M. D., R. S. Tarng, and D. C. Rio. 1997. The alternative splicing factor PSI regulates P-element third intron splicing in vivo. Genes. Dev. 11:129-138. - PubMed
-
- Bassell, G. J., and R. H. Singer. 2001. Neuronal RNA localization and the cytoskeleton. Probl. Cell Differ. 34:41-56. - PubMed
-
- Carey, J., V. Cameron, P. L. de Haseth, and O. C. Uhlenbeck. 1983. Sequence-specific interaction of R17 coat protein with its ribonucleic acid binding site. Biochemistry 22:2601-2610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
