Suppression of p53-dependent senescence by the JNK signal transduction pathway
- PMID: 17893331
- PMCID: PMC2000443
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707782104
Suppression of p53-dependent senescence by the JNK signal transduction pathway
Abstract
The JNK signaling pathway is implicated in the regulation of the AP1 transcription factor and cell proliferation. Here, we examine the role of JNK by using conditional and chemical genetic alleles of the ubiquitously expressed murine genes that encode the isoforms JNK1 and JNK2. Our analysis demonstrates that JNK is not essential for proliferation. However, JNK is required for expression of the cJun and JunD components of the AP1 transcription factor, and JNK-deficient cells exhibit early p53-dependent senescence. These data demonstrate that JNK can act as a negative regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
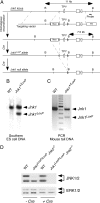
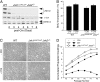
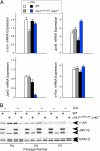
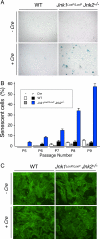
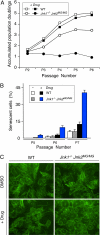
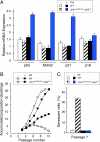
References
-
- Davis RJ. Cell. 2000;103:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Jochum W, Passegue E, Wagner EF. Oncogene. 2001;20:2401–2412. - PubMed
-
- Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA, Davis RJ. Science. 2000;288:870–874. - PubMed
-
- Manning AM, Davis RJ. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:554–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

